Fig. 4. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis.
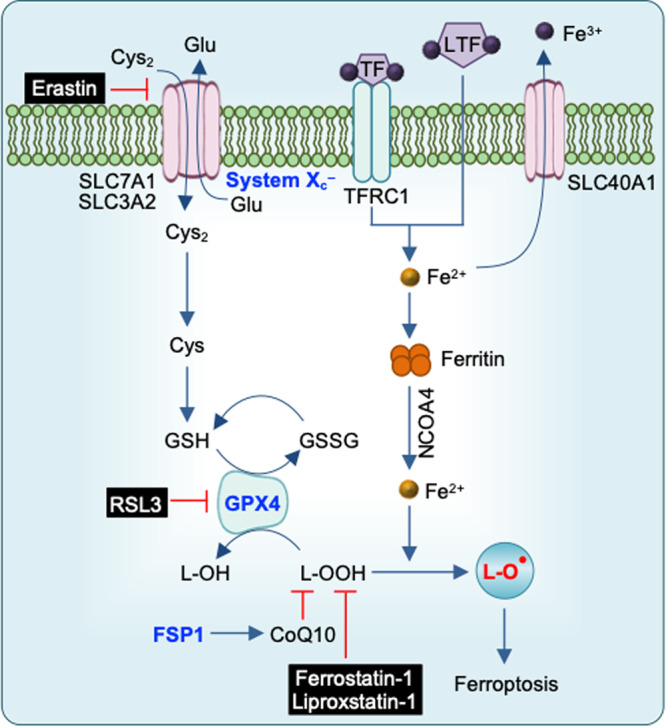
Ferroptosis is primarily driven by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. Iron bound to transferrin is transported into cells by TFRC1. NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy increases the free iron pool. Ferroptosis is inhibited by GSH, the synthesis of which involves the uptake of cystine via the cystine-glutamate antiporter (system Xc-). Using GSH as a cofactor, GPX4 reduces phospholipid hydroperoxides to their corresponding alcohols. The FSP1-CoQ10 system inhibits ferroptosis.
