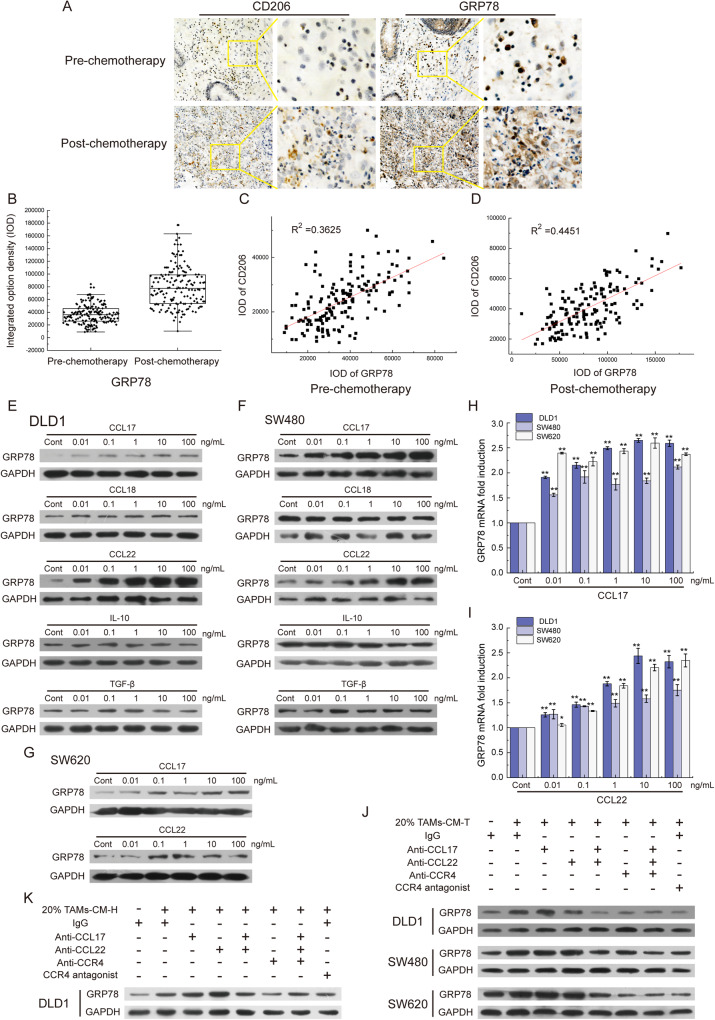
Fig. 3. The CCL17/CCL22-CCR4 axis was responsible for GRP78 expression.
A The level of GRP78 protein and the infiltration of TAMs (Marked with CD206) were detected in clinical samples by IHC. B The statistics of the integrated option density (IOD) of the brown areas in A. C The graph represented the correlation of GRP78 and CD206 in pre-chemotherapy colorectal tumors. D The correlation analysis of GRP78 and CD206 in post-chemotherapy colorectal tumors. E The level of GRP78 protein was detected in DLD1 cells treated with CCL17, CCL18, CCL22, IL-10, and TGF-β. F The level of GRP78 protein was detected in SW480 cells treated with CCL17, CCL18, CCL22, IL-10, and TGF-β. G The level of GRP78 protein was detected in SW620 cells treated with CCL17 and CCL22. H The level of GRP78 mRNA was detected in DLD1, SW480, and SW620 cells treated with CCL17 by qRT-PCR, **p < 0.01. I The level of GRP78 mRNA was detected in DLD1, SW480, and SW620 cells treated with CCL22 by qRT-PCR, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. J The level of GRP78 protein was detected in DLD1, SW480, and SW620 cells with 20% TAMs-CM-T treatment. Antibodies against CCL17, CCL22, and CCR4 and the CCR4 antagonist were applied to block the CCL17/CCL22-CCR4 pathway. K The level of GRP78 protein was detected in DLD1 cells with 20% TAMs-CM-H treatment. Antibodies against CCL17, CCL22, and CCR4 and the CCR4 antagonist were applied to block the CCL17/CCL22-CCR4 pathway.