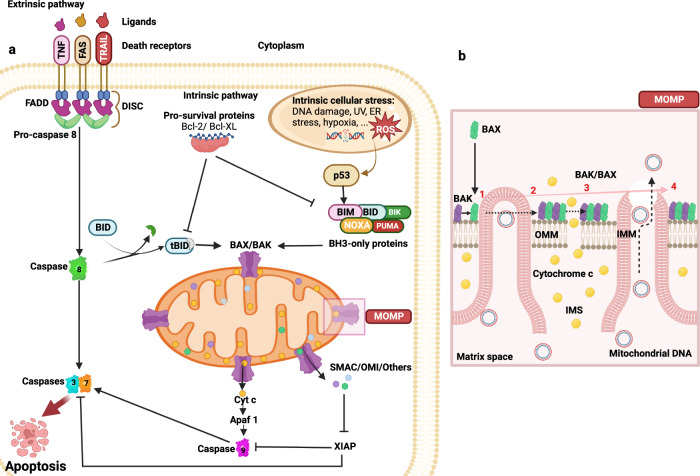
Fig. 4. Apoptotic signaling pathways.
a In the extrinsic pathways, death receptor ligands bind to members of the death receptor family to function, for instance, TNF, FAS, and TRAIL receptors. Numerous diverse stressors, such as DNA damage, the removal of growth factors, and mitotic arrest, activate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, which in turn activates BH3-only members. By activating the effector proapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins Bax and Bak and inhibiting antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, BH3-only proteins cause MOMP. In particular, cyt c is activated by releasing proteins from the mitochondrial intermembrane gap. The heptameric structure known as the apoptosome is created when cyt c interacts with APAF1. As a result, caspase-9 is recruited and activated, which cleaves and activates caspase-3 and -7. The caspase inhibitor XIAP is blocked by proteins such as SMAC, which are released due to MOMP, promoting apoptosis. The extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways are linked via caspase-8 cleavage and activation of the BH3-only protein Bid. b In normal cases, Bax localizes to the cytoplasm and Bak to the mitochondria. By interacting with BH3-only proteins, Bax and Bak can be directly activated during apoptosis, which leads to their stabilization on the OMM. Their dimer further oligomerizes into a higher-order multimer, contributing to the release of cyt c and other IMS proteins. Over time, Bax and Bak accumulate with macropore formation, which allows the IMM to protrude through the OMM, after which the IMM herniates and ruptures, eventually releasing mtDNA. TNF Tumor Necrosis Factor, FADD Fas-Associated Protein with DD, DISC Death-Inducing Signaling Complex, TRAIL Tumor necrosis factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand, SMAC Second Mitochondria-derived Activator of Caspases, tBid truncated Bid, Apaf1 Apoptotic protease-activating Factor 1, XIAP X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein, PUMA p53 Upregulated Modulator of Apoptosis, UV Ultraviolet.