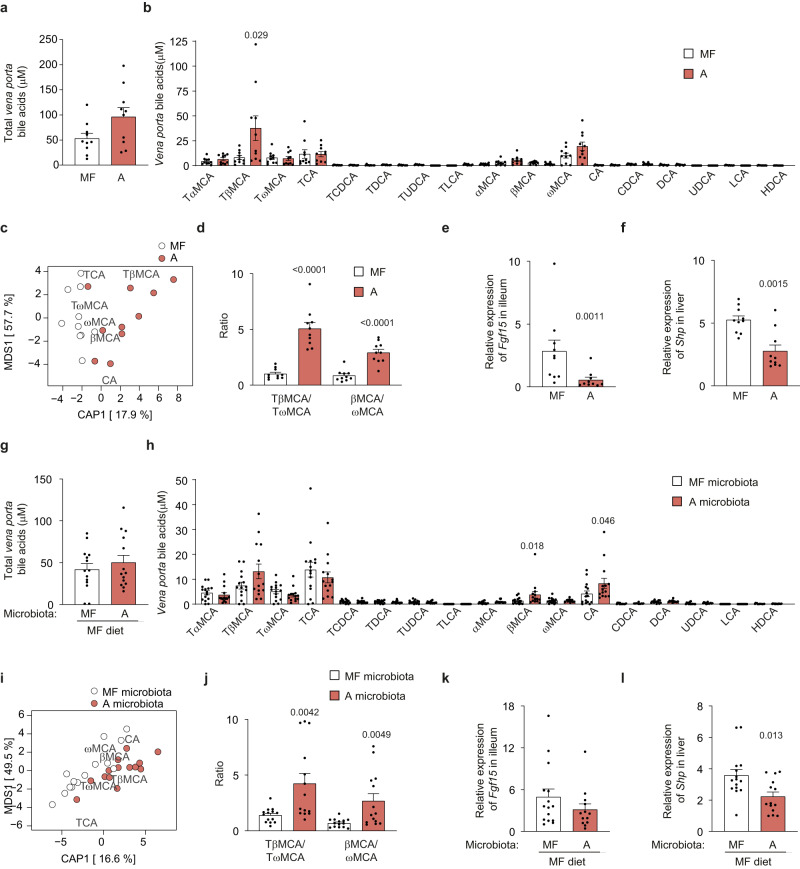
Fig. 8. The cecal microbiota from mice fed diet A regulates vena porta bile acid levels and hepatic expression of Shp in mice fed the MF diet.
Bile acid levels and expression of genes regulated by bile acids in mice fed diet A or MF diet for 9 weeks (a–f) and in mice inoculated with cecal microbiota from mice fed MF or A diet and subsequently fed MF diet for 9 weeks (g–l). a Total vena porta bile acid levels, b vena porta levels of individual bile acids, c redundancy analysis (RDA) plot based on relative bile acid levels in vena porta, d TβMCA/TωMCA and βMCA/ωMCA ratios, e relative ileum expression of Fgf15 and f relative hepatic expression of Shp in mice fed diet A or MF diet. g Total vena porta bile acid levels, h vena porta levels of individual bile acids, i redundancy analysis (RDA) plot based on relative bile acid levels in vena porta, j TβMCA/TωMCA and βMCA/ωMCA ratios, k relative ileum expression of Fgf15, and l relative liver expression of Shp in mice inoculated with cecal microbiota from mice fed MF or A diet and subsequently fed MF diet. a–f: n = 10; g–l: n = 15 (MF microbiota), 14 (A microbiota) except for k where n = 13 for A microbiota. Significant p-values determined by two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test are displayed in the figure. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. MCA muricholic acid, CA cholic acid, CDCA chenodeoxycholic acid, DCA deoxycholic acid, UDCA ursodeoxycholic acid, LCA lithocholic acid, HDCA hyodeoxycholic acid, T taurine-conjugated species, Fgf15 fibroblast growth factor 15, Shp small heterodimer partner. Source data are provided as a Source data file.