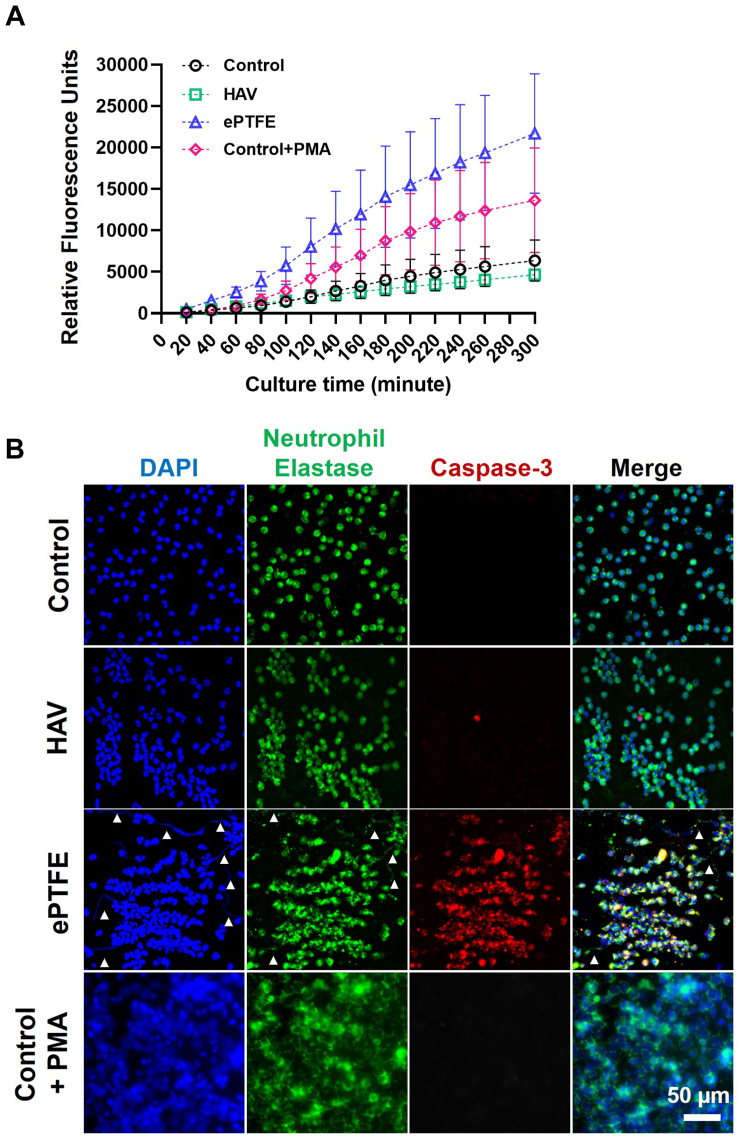
Fig 5.
Neutrophil elastase release after contact with human acellular vessel (HAV) and expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE). (A) Real-time monitoring of neutrophil elastase release by MeOSuc-AAPV-AMC fluorescence in the presence of DNAse I after seeding neutrophils onto HAV, ePTFE, and control substrates, with and without phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) stimulation. Data are mean ± standard error from six experiments with three replicates for each condition. (B) Representative images of neutrophil elastase (green) and caspase-3 (red) immunostaining at 3 hours after seeding onto control, HAV, ePTFE, and control with PMA (100 ng/mL). Nuclei (blue) counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). The white arrowheads in ePTFE samples show extracellular DNA or neutrophil elastase within neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs).