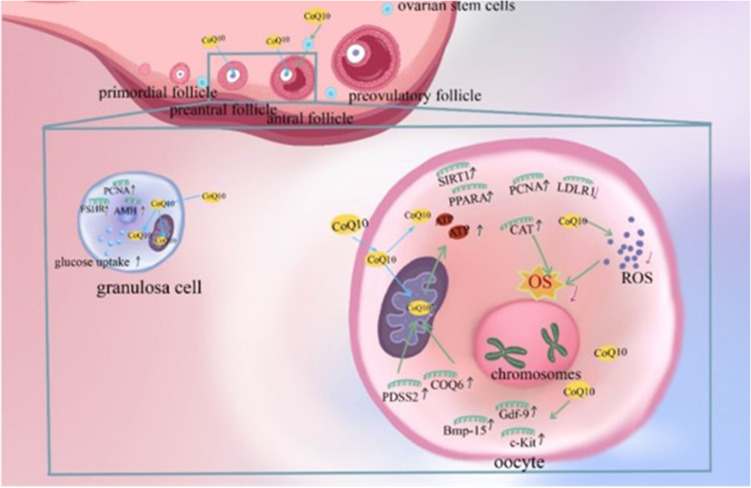
Figure 2.
Mechanism of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) improving ovulation disorders. CoQ10 has the ability to promote ovarian stem cells differentiation and support function of oocytes and granulosa cells.63 Polyprenyl diphosphate synthase subunit 2 (PDSS2) and Coenzyme Q6 (COQ6) are key genes for the synthesis of CoQ10.50 In oocytes, CoQ10 enhances mitochondrial function, promotes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and oxidative stress (OS), and decreases the rate of chromosomal aneuploidy.6,84 In addition, it stimulates the expression of growth differentiation factor 9 (Gdf-9), bone morphogenetic protein 15 (Bmp-15), KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase (c-Kit) and Catalas (CAT) genes related to oocyte quality and regulates the expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor 1(LDLR1), Peroxisome (PPARA) and sirtuin 1(SIRT1) genes related to metabolism.64–66,85,90 In granulosa cells, CoQ10 promotes follicle-stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR), anti-müllerian hormone (AMH) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression and increases cellular uptake of glucose.61,63 Through the above possible mechanisms eventually enhance the quality of oocytes and granulosa cells, increase the number of oocytes, which is beneficial to the functional reserve of the ovary.