Table 3.
Complex epilepsy surgery cases with IONM.
| Clinical data | Pre-operative MRI | Post-operative CT/MRI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | Pathology: Residual left-hemispheric pathology. |
|
|
| M, 12 years | Seizures: Daily asymmetric tonic spasms provoked by unexpected tactile and auditory stimuli. | ||
| Neurological examination: Mild right-sided hemiparesis. | |||
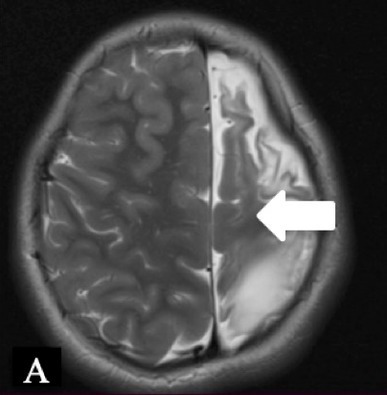
| MRI: Axial T2 with a small cortical remnant on the left parasagittal (white arrow in Figure A). | |||
| Wada test: Confirmed right leg motor functionality of the parasaggital cortical remnant. | |||
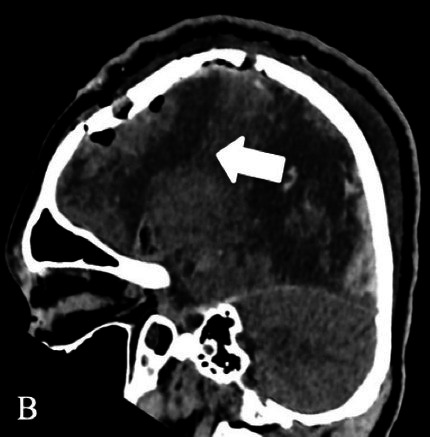
| Surgery: Modified hemispherotomy after intra-operative monitoring (IONM) and preservation of the right leg motor function (early sagittal CT showing the descending fibers from that area, white arrow on Figure B). | |||
| Follow-up: Early postoperative seizures for 1 week, then >1 year seizure-free. | |||
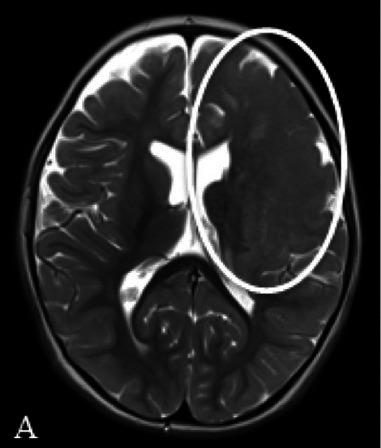
| Patient 2 | Pathology: Large cortical malformation of the left hemisphere (white oval on axial T2-MRI, Figure A1). |
|
|
| F, 2 years | Seizures: Daily asymmetric spasms and right hemifacial seizures | ||
| Neurological examination: Normal | |||
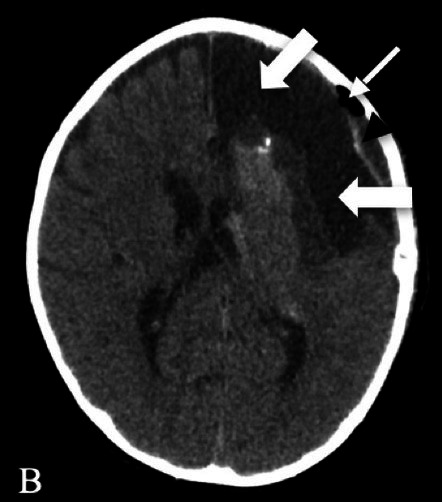
| Surgery: IONM during extensive frontal lobectomy up to the motor cortex; and temporal disconnection. Early postoperative axial CT scan (Figure B1) demonstrating the cystic cavity on the left frontal (bold white arrow) and small subdural hygroma with air collection (thin white arrows). | |||
| Follow-u p: No motor deficit. Early postoperative seizures with excellent effect of Carbamazepine introduction. | |||
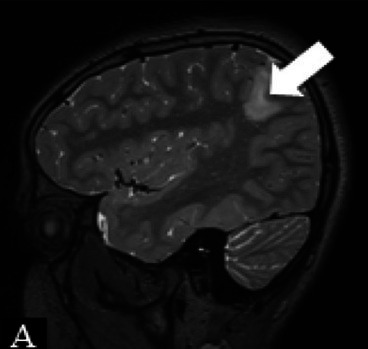
| Patient 3 | Pathology: Left parietal tumor adjacent to eloquent areas (supramarginal gyrus) as seen on sagittal T2-MRI (hyperintensity lesion, white arrow, Figure A2). |
|
|
| Seizures: Head deviation to the right with bilateralization. | |||
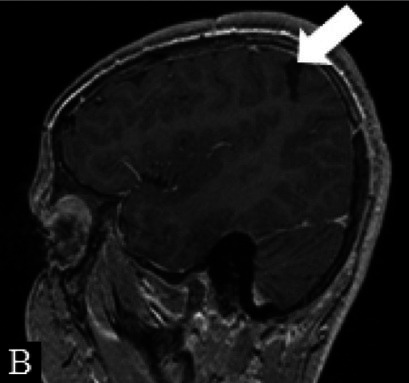
| M, 13 years | Surgery: Awake craniotomy with IONM and simultaneous testing of language functions allowed complete tumor resection (white arrow on sagittal and thin cystic cavity on 6-month post-operative contrast-enhanced T1-MRI, Figure B2). | ||
| Follow-up: Seizure-free and no ASM for >5 years. |
