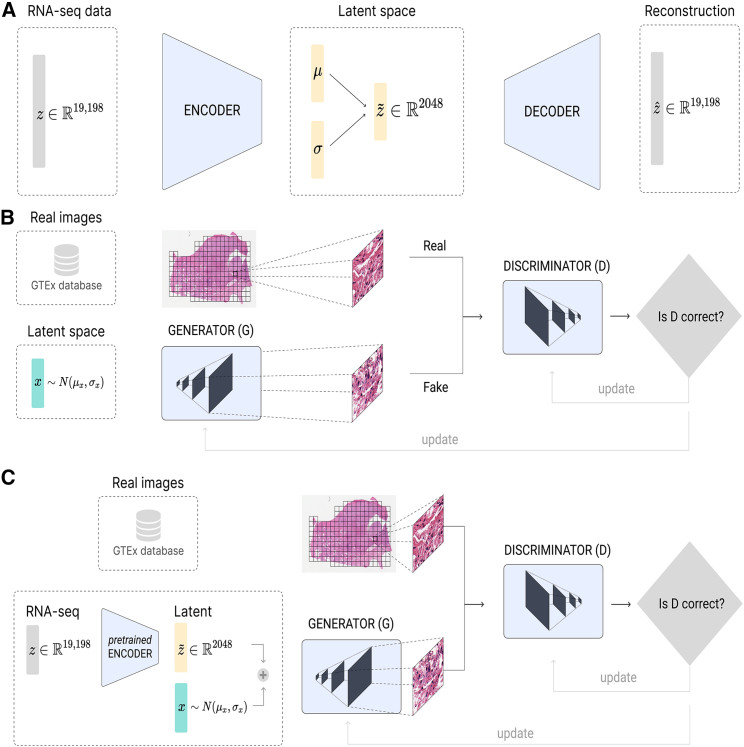
Figure 1.
Model architecture for gene expression, WSIs, and combined data using VAE and GANs
(A) β-VAE architecture for the generation of synthetic gene expression data. The model uses as input the expression of 19,198 genes. Both the encoder and the decoder are formed by two linear layers of 6,000 and 4,096, respectively. The latent μ and σ vectors have a feature size of 2,048.
(B) GAN architecture for generating tiles by sampling from a random normal distribution. The architecture chosen was a deep convolutional GAN (DCGAN),45 using as input a feature vector of size 2,048. The final size of the tiles generated is 256 × 256, the same as the size of the real tiles.
(C) RNA-GAN architecture where the latent representation of the gene expression is used for generating tiles. The gene expression profile of the patient is used in the β-VAE architecture to obtain the latent representation. Then, a feature vector is sampled from a scaled random normal distribution (values ranging between [−0.3,0.3]) and added to the latent representation. A DCGAN is trained to use this vector as input and generate a 256 × 256 sample. The discriminator receives synthetic and real samples of that size.