Figure 2.
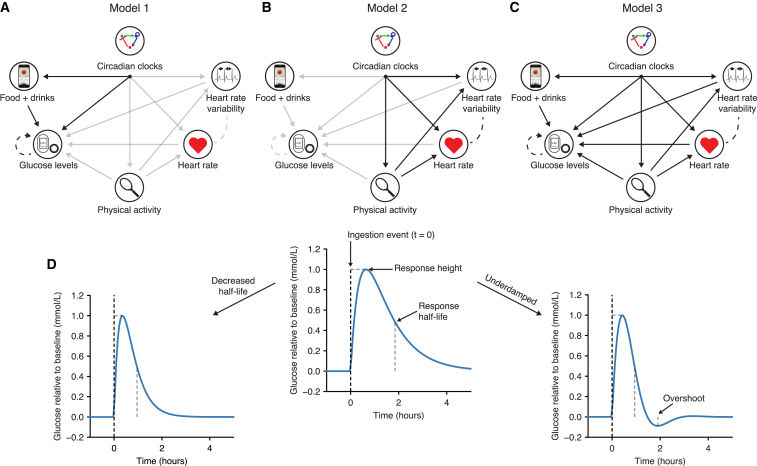
Schematic showing the three different models and parameter interpretation
(A–C) The glucose and ingestion events interaction model (A, model 1), the physical and heart activity interaction model (B, model 2), and the full model (C, model 3). Solid arrows represent direct unidirectional influences, while dashed lines represent correlated fluctuations that are not specifically directional.
(D) A meal or drink event causes a glucose increase to a specific meal height relative to the baseline glucose value. The response half-life determines how quickly glucose returns to baseline. Underdamping (defined as a negative damping coefficient) leads to an overshoot below the baseline values.