Figure 1.
Comparison between sci-Plex and 10×
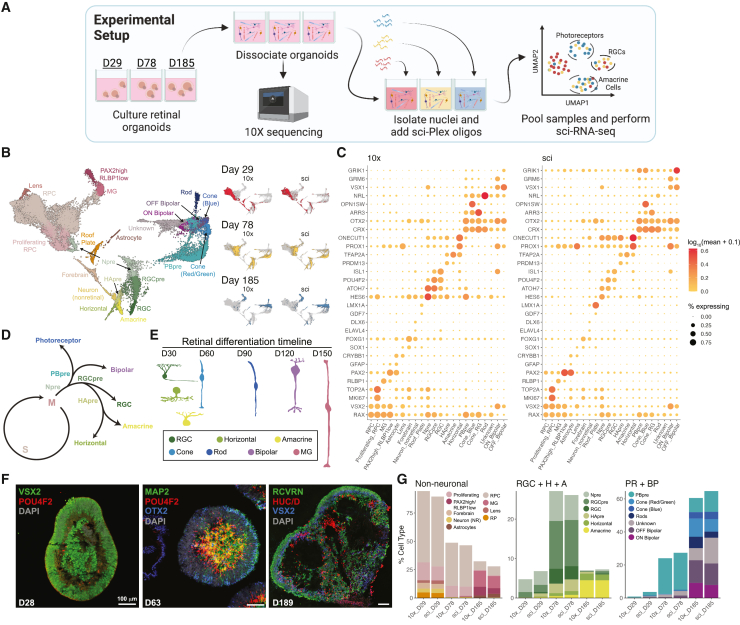
(A) Retinal organoids were cultured for 29, 78, or 185 days. The cells were split and either processed by a 10× RNA-seq pipeline or prepared by sci-Plex.
(B) Integrated UMAP of sci-Plex and 10× datasets. Left: cells colored by cell type. RPC, retinal progenitor cell; MG, Müller glia; Npre, retinal neuronal precursor; RGC, retinal ganglion cell; RGCpre, RGC precursor; HApre, horizontal/amacrine precursor; PBpre, photoreceptor/bipolar precursor. Right: cells are faceted by organoid age and technology. Cells are colored by age.
(C) Dot plot of genes used to define cell types in (B). Dot size indicates the percentage of cells that express the gene of interest. Color indicates the log10 mean UMIs per cell.
(D) Representation of retinal neuron developmental trajectories.
(E) Timeline of retinal cell differentiation in human organoids.
(F) Immunostaining of day 28, 63, and 189 organoids for progenitor (VSX2-day 28), RGC (POU4F2), photoreceptor/bipolar (OTX2), neuronal (MAP2), amacrine/horizontal/RGC (HuC/D), bipolar cell (VSX2-day 189), and photoreceptor (RCVRN) markers. Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(G) Using the cell-type assignments from (B), cells were counted, and the percentage of cell type was determined for each technology and organoid age.