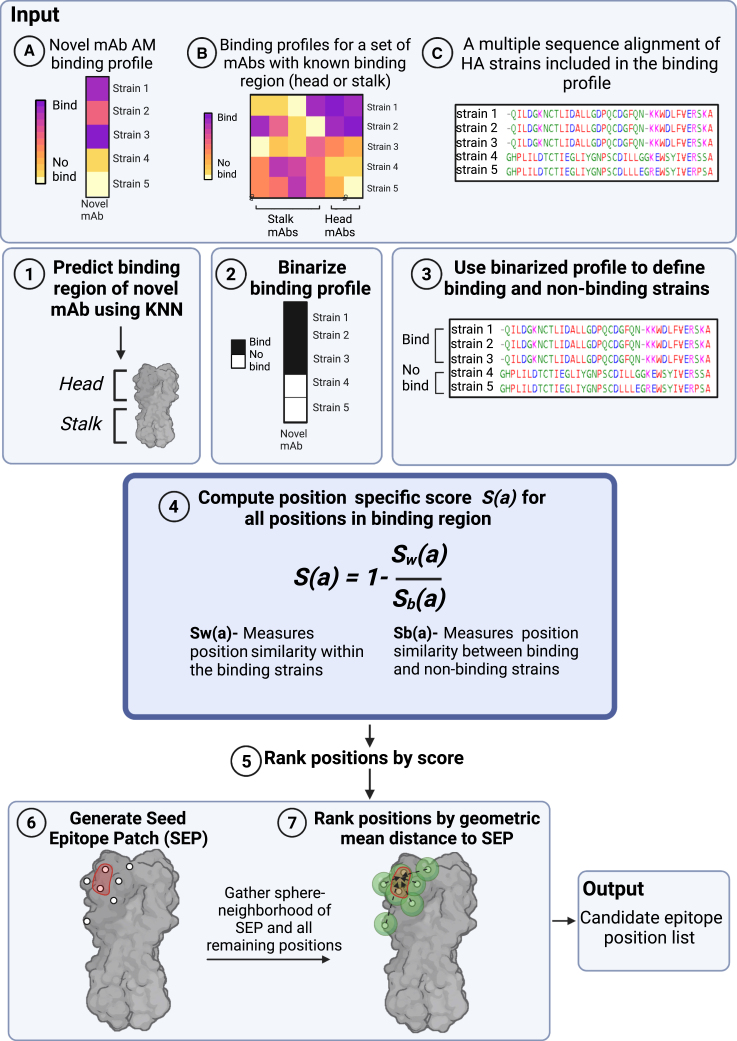
Figure 4.
The mAb-Patch epitope prediction algorithm
The algorithm receives three inputs: (A) the binding profile of a novel mAb, generated using an AM; (B) AM binding profiles for a set of mAbs with known binding regions (head or stalk) across a set of HA strains, and (C) a multiple sequence alignment of the HA strains included in binding profile (A). Using these inputs, the algorithm includes the following steps: (1) classify binding region (head vs. stalk) of novel mAb using KNN classification using known mAb binding profiles (input B). (2) Binarize binding profile A using a predefined threshold. (3) Use binarized profile to define binding and non-binding HA strains. (4) Compute position-specific score, S(a), based on the ratio between the similarity between all pairs of amino acids from binding strains (Sw) and all pairs of amino acids from binding and non-binding strains (Sb). (5) Rank all positions in binding region by their score (6) Use the top ranked positions to define the seed epitope patch (SEP). (7) Rank all other positions withing the binding region by their geometric mean distance from the center of the SEP. Output-candidate epitope position list based on top ranked positions.