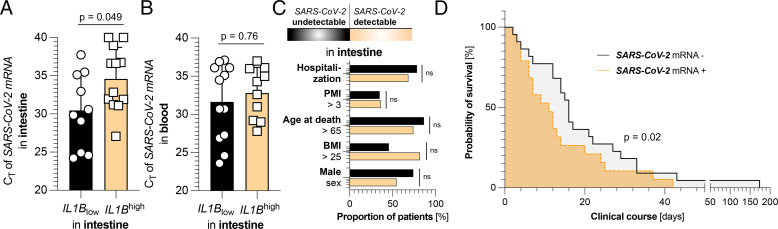
FIGURE 4.
High levels of IL-1B in the intestine are associated with a reduced viral load among individuals with detectable SARS-CoV-2 infection of the intestine. (A) CT values of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA expression in the intestines of patients with a detectable SARS-CoV-2 viral load (n = 22), divided according to low (below the median of all 44 patients, black, n = 10) and high (above the median of all 44 patients, yellow, n = 12) expression of intestinal IL1B. (B) CT values of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA expression in the blood of patients with a detectable SARS-CoV-2 viral load (n = 22), divided according to low (below the median of all 44 patients, black, n = 12) and high (above the median of all 44 patients, yellow, n = 10) expression of intestinal IL1B. (C) Cohort characteristics of patients with undetectable (n = 23, black) and detectable (n = 22, yellow) intestinal SARS-CoV-2 viral loads. (D) Kaplan-Meier analysis of survival length in patient cohorts divided according to the absence (n = 23, black) or detectability (n = 22, yellow) of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA in the intestine. The p values were corrected for multiple testing when appropriate. Horizontal lines represent the mean ± SEM; each symbol indicates one sample from one patient.