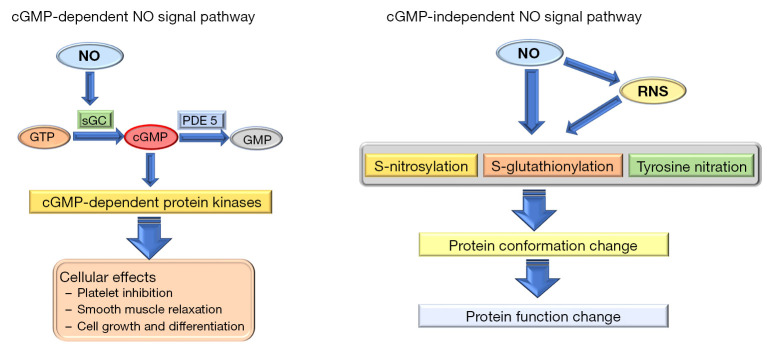
Figure 2.
cGMP-dependent and cGMP-independent pathways of nitric oxide signals. In the cGMP-dependent pathway, the signal of NO is converted to increased cGMP concentration by activation of soluble guanylate cyclase. Increased cellular cGMP activates various protein kinases in the cell. The major effect of NO via the cGMP-dependent pathway includes inhibition of platelet aggregation, smooth muscle relaxation, and cell growth and differentiation. In the cGMP independent pathway, the NO signal modifies the protein structure via S-nitrosylation, S-glutathionylation, and tyrosine nitration. Confirmation change in cellular protein results in the alteration of functional activity. cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; NO, nitric oxide; sGC, soluble guanylate cyclase; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; GMP, guanosine monophosphate; PDE5, phosphodiesterase 5; RNS, reactive nitrogen species.