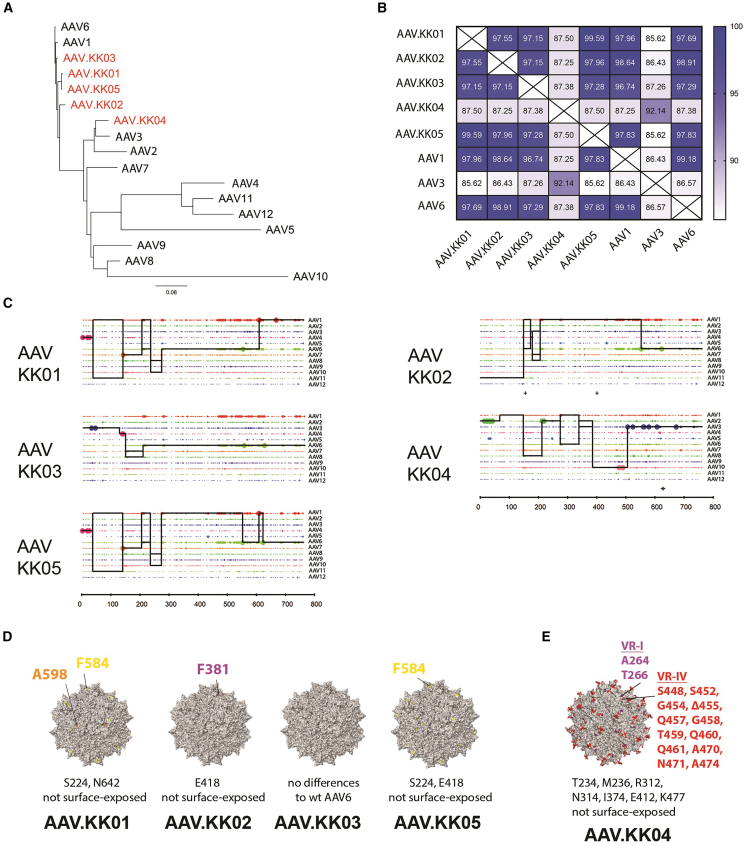
Figure 1.
Cardiotropic rAAV variants obtained by directed evolution were closely related to WT AAV6 and AAV3
Directed evolution was performed using the hiPSC-CM line WTCWT. After six rounds of selection, the enriched novel AAVs were sequenced and phylogenetic analysis performed to compare with parental AAVs. (A) Clustering of amino acid sequences from novel variants (red) to WT AAV parental serotypes (black), with relationships depicted as a phylogenetic tree. (B) Heatmap illustrating the percentage identity among select parental AAVs and enriched novel variants. (C) Parental sequence contribution analysis of variants isolated after directed evolution. Black line represents the most probable composition of individual shuffled clones based on the longest sequence of identity to parental variants in a 5′ to 3′ direction. (D) Surface representations of the new capsid variants KK01, KK02, KK03, and KK05. The colored regions (yellow, orange, purple) denote surface residues that differ from the parental AAV6 capsid. Amino acid changes not located on the capsid surface are listed below. (D) Depiction as in (E) for the capsid variant KK04. The colored regions (red and purple) denote surface residues that differ from the parental AAV3b capsid. See also Figure S1.