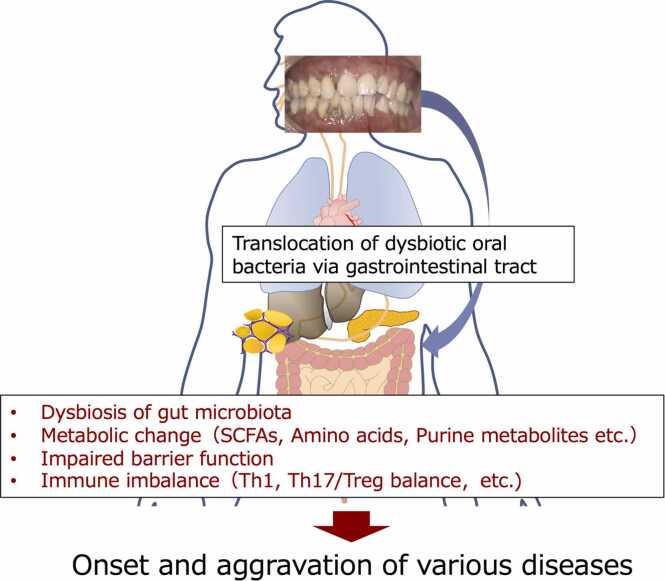
Fig. 2.
Effect of oral dysbiosis on gut ecosystem. Dysbiotic oral microbiota is considered to affect gut microbiota resulting in 1) disruption of gut barrier function, leading to endotoxemia, systemic inflammation, and other consequences; 2) effects on gut immunity, including an increase in Th1 and Th17 responses, as well as a decrease in Treg responses; and 3) changes in bacterial metabolites, such as a decrease in short-chain fatty acids and an increase in secondary bile acids, branched-chain amino acids, and aromatic amino acids. Th, T helper. SCFAs, Short-chain fatty acids.