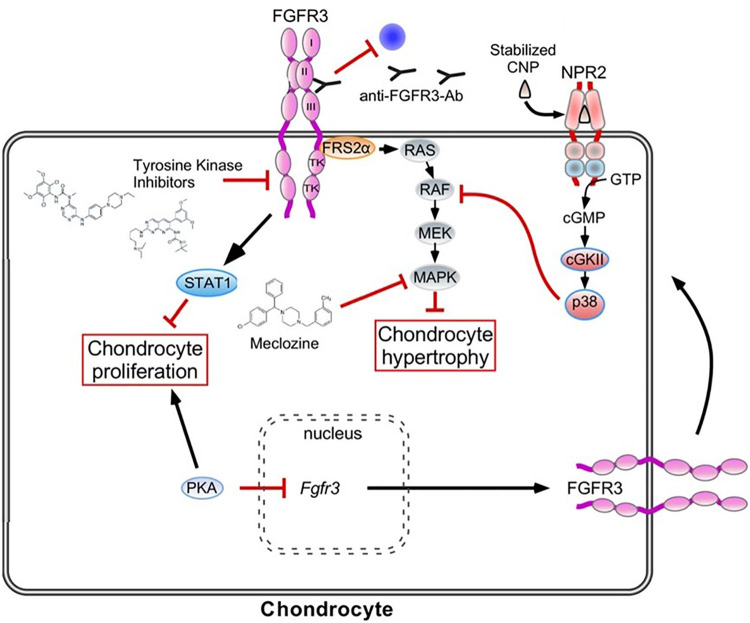
Figure 6.
Achondroplasia is the most common genetic disorder of chondrogenesis. This figure outlines the primary pathway for its pathoetiology (gain of function of FGFR3 receptor which inhibits chondrocyte hypertrophy and maturation through the RAS pathway and inhibits chondrocyte proliferation through the STAT1 pathway) Therapeutic options include Vosoritide which is a synthetic CNP that in turn inhibits the RAS pathway. Additional CNP mediators are under investigation. The off-label use of Meclizine, a common anti-emetic is in clinical trial as a therapeutic option as it has been found to inhibit the RAS pathway. Antibodies targeted at the FGFR3 receptor are also under investigation in an attempt to reduce the overactive ligand that results in the Achondroplasia phenotype. (Figure adapted from Achondroplasia: Development, pathogenesis and Therapy) (32).