Figure 1.
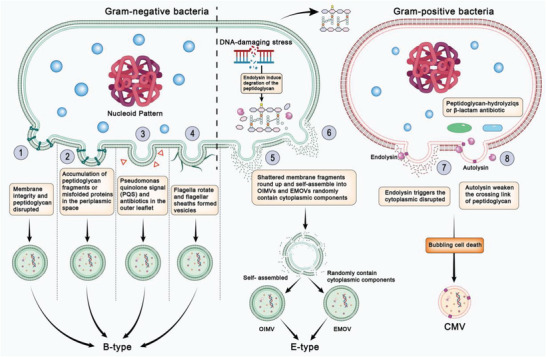
Schematic diagram of different biogenesis of bacterial membrane vesicles. 1) Crosslinking between peptidoglycan and the outer membrane integrity is disrupted due to various stressful responses of bacteria. 2) Accumulation of peptidoglycan fragments or misfolded proteins in the periplasmic space. 3) Quorum‐sensing molecule Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) or antibiotics destabilize the biochemical structure. 4) Bacterial flagella surrounded by a sheath rotating along the membrane blebs. 5) Shattered membrane fragments round up and self‐assemble into OIMVs from explosive cell lysis triggered by genotoxic stress. 6) Cytoplasmic components randomly assembled into EOMVs. 7) Endolysins weaken peptidoglycan and trigger the production of explosive CMVs. 8) Autolysins weaken the crosslinking of the peptidoglycan and modulate CMV release through the cell wall.
