Figure 5.
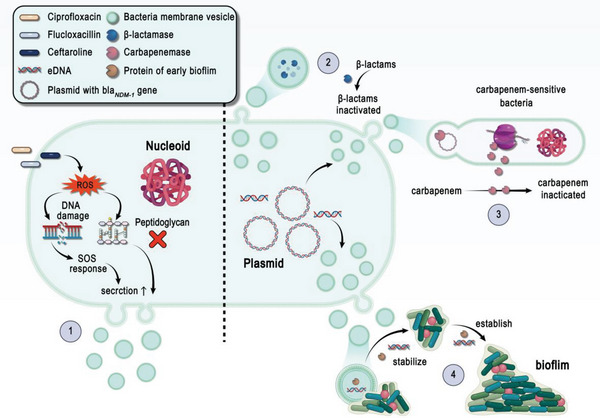
A schematic of the mechanisms involved in antibiotic resistance and bacterial vesicles. 1) On the left of the dotted line, ciprofloxacin triggers the SOS response to weaken the Gram‐positive bacterial cell wall, concomitant with strong induction of vesicle formation by flucloxacillin or ceftaroline. 2) On the right of the dotted line, BMVs can carry antibiotics contained with β‐lactamase and glycopeptides functional groups and further neutralize or hydrolyze antibiotics. 3) BMVs can mediate horizontal gene transfer (HGT) to help bacteria acquire antibiotic resistance. and 4) BMVs can help bacteria stabilize and establish biofilms and further induce the broad‐spectrum resistance to antibiotics.
