Figure 2.
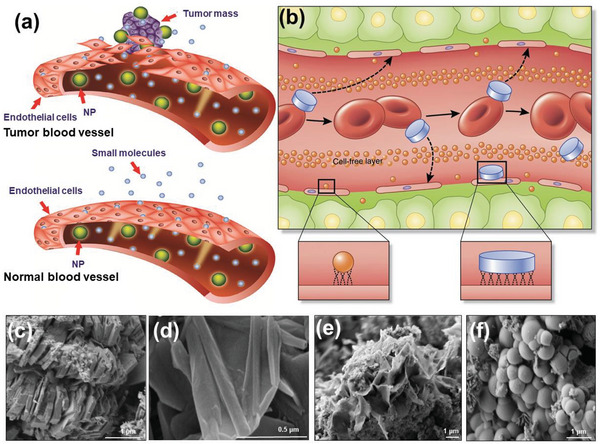
a) Tumor blood vessels have large openings between endothelial cells (ECs), allowing NPs to reach the stroma and tumor cells. In contrast, normal tissues contain tightly connected ECs that prevent the diffusion of NPs from blood vessels. a) Reproduced with permission.[ 77 ] Copyright 2015, Dove Medical Press Ltd). b) Longitudinal cross‐sectional illustration of a blood vessel containing circulating red blood cells (red, oval shapes), spherical particles (orange), and discoidal particles (blue, rectangle shapes) that travel through and adhere to the walls. Margination inset (right): lateral drifting of discoidal particles promotes periodic interaction with the vessel walls; margination inset (left): limited size and surface area of conventional spherical NPs contacting with ECs. Reproduced with permission.[ 78 ] Copyright 2015, Springer Nature. c) The common booklet‐like shape of Kaol. d) The tubular morphology of Kaol treated by chemical modification. c,d) Reproduced with permission.[ 79 ] Copyright 2015, Elsevier. Synthesis results of e) sponge‐shaped and f) spherical Kaol. Reproduced with permission.[ 80 ] Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
