Figure 1. Overview of TBDA activities.
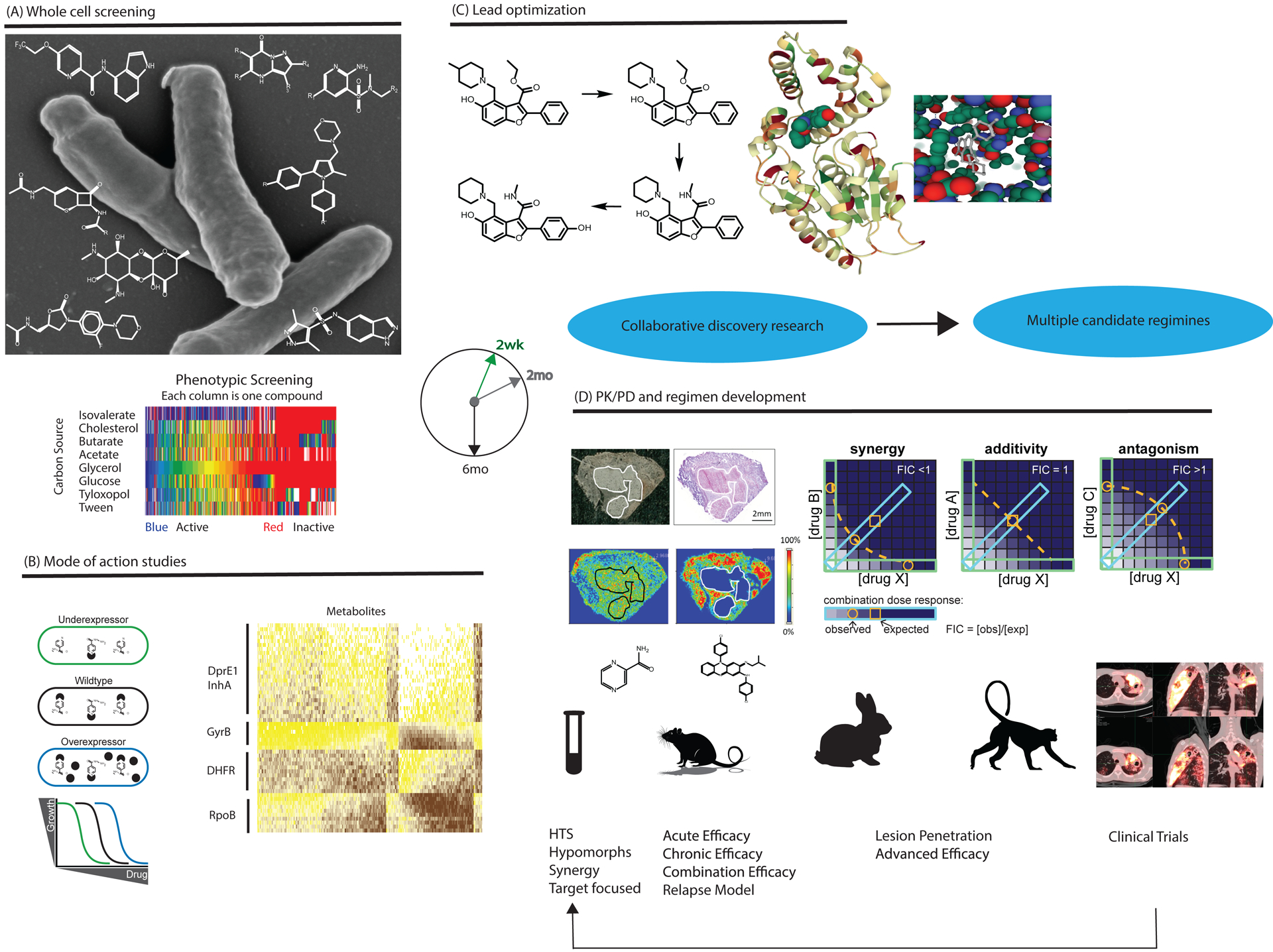
A. Phenotypic whole cell screening of Mtb against substantial chemical diversity. Examples of hit series from TBDA screening programs are shown against a scanning electron microscopy image of the pathogen. TBDA screens use diverse biological conditions illustrated by the heat map showing divergent results from screening the same compound deck against Mtb grown with different nutrients. B. Genetics and metabolomics facilitate studies of mechanism of action. For example, strains under- and over-expressing the target show selectively differential responses to an inhibitor of that target (left), while novel inhibitors of a pathway often elicit metabolomic responses similar to those seen with known inhibitors of the same pathway (right). C. Advanced series enter lead optimization with crystallography support, as illustrated for PKS 13 inhibitors. D. Advances in preclinical tools for evaluating new regimens include imaging mass spectrometry to quantify drug penetration into TB lesions and new approaches to measure synergies and antagonisms among multiple agents. Higher animal models of TB are studied with the same tools applied in early human studies, helping to develop better preclinical tools to predict treatment responses in humans. Lessons from clinical trials are applied to the ongoing process of drug discovery. (All studies involving animals were ethically reviewed and conducted in accordance with the relevant institution’s policy on the care, welfare and treatment of laboratory animals.)
