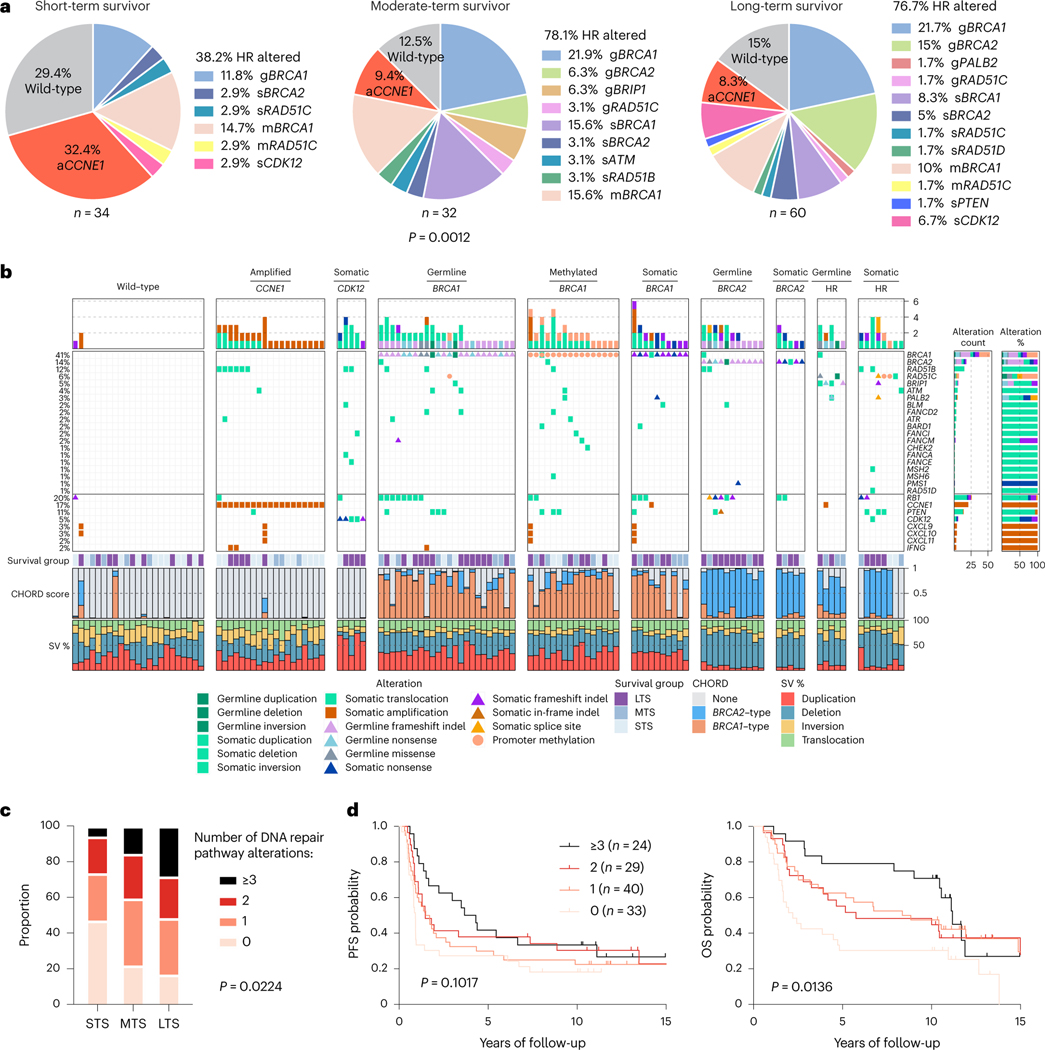
Fig. 1 |. HGSCs with multiple altered DNA repair pathway genes are associated with long-term survival.
a, Proportion of patients affected by homologous recombination (HR) DNA repair pathway gene alterations and CCNE1 gene amplification (aCCNE1) in each survival group. Homologous recombination alterations include pathogenic germline (g) or somatic (s) mutations, and BRCA1 or RAD51C promoter methylation (m) as indicated. One alteration is counted for patients with more than one change, prioritizing alterations by variant allele frequency and/or by evidence of genomic scarring associated with the candidate driver alteration. Differences in proportions of homologous recombination-altered, CCNE1 amplified and wild-type tumors between survival groups were assessed by chi-square. b, Bars at the top represent the number of alterations in each listed gene per patient. Pathogenic germline and somatic alterations in homologous recombination pathway genes are shown, as well as alterations in other DNA repair associated genes, immune genes and CCNE1. Each patient (column) is annotated with survival group (LTS, long-term survivor; MTS, moderate-term survivor; STS, short-term survivor). Bars indicate the level of homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) in each primary tumor sample, measured as probabilities of BRCA1-type (orange) HRD, BRCA2-type(blue) HRD, or homologous recombination proficiency (none, gray), as predicted by CHORD28. Bar plots at the bottom indicate the proportion of total detected structural variants (SV) classified as duplications, deletions, inversions or interchromosomal translocations. Samples are grouped by the primary gene alteration identified in each patient. Alteration count and proportion of alteration types per gene are shown as bar plots on the right. c, Proportion of patients with 0, 1, 2 or 3 or more DNA repair pathway alterations by survival group (LTS, long-term survivor; MTS, moderate-term survivor; STS, short-term survivor). Differences in proportions between groups were assessed by chi-square. d, Kaplan-Meier analysis of progression-free survival (PFS) (left) and OS in patients (right) with 0, 1, 2 or 3 or more DNA repair pathway alterations. P values calculated by Mantel-Cox log-rank test.