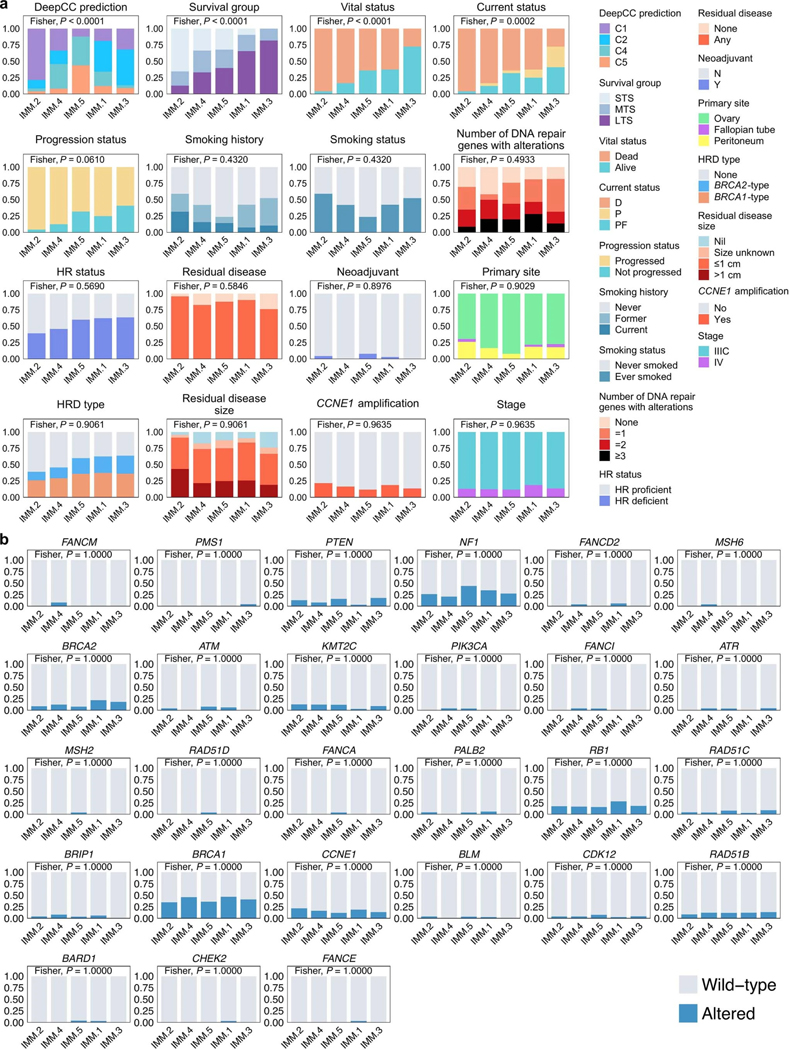
Extended Data Fig. 9: Categorical features of immune clusters.
a, Proportion of patients with categorical features per cluster. Features are ordered by significance using Fisher’s exact test (two-sided) and the clusters are arranged by the proportion of long-term survivors. Features include homologous recombination (HR) status, homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) type, number of DNA repair pathway alterations, survival group (LTS, long-term survivor; MTS, moderate-term survivor; STS, short-term survivor), status at last follow-up (D, dead; P, progressed and alive; PF, progression-free and alive), self-reported smoking status, DeepCC molecular subtype (C1, mesenchymal; C2, immunoreactive; C4, differentiated; C5, proliferative), and neoadjuvant treatment (Y, yes; N, no). b, Proportion of patients affected by gene alterations per immune cluster. Genes are ordered by significance using Fisher’s exact test (two-sided) and clusters are ordered by the proportion of long-term survivors. The Fisher’s test P values displayed in (a) and (b) are Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted P values.