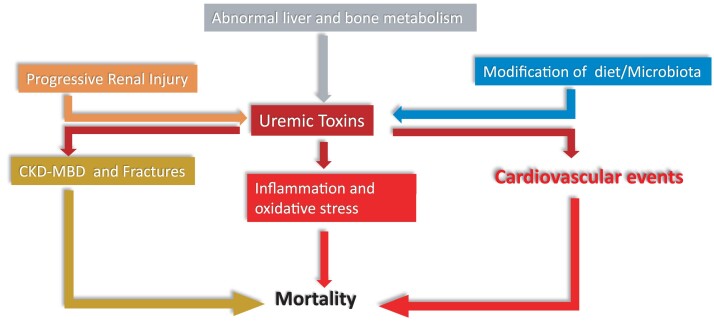
Figure 7.
Multiple inter-relationships between uremic toxins, derangements in endocrine control, inflammation and oxidative stress impinging upon cardiovascular risk in CKD. ‘Progressive renal injury, which facilitates accumulation of uremic toxins, and alterations in the gut microbiota, which increase the synthesis of the same compounds, are main factors for the high levels of uremic toxins in CKD patients and alterations in liver and bone metabolism contribute to this process. Uremic toxins incite inflammation and cardiovascular events and contribute to the chronic kidney disease -metabolic bone disorder (CKD-MBD) and the resulting high risk for fractures of CKD patients. Inflammation, the CKD-MBD disorder and the high risk for cardiovascular events all conjure in causing a high death risk in the CKD population’.