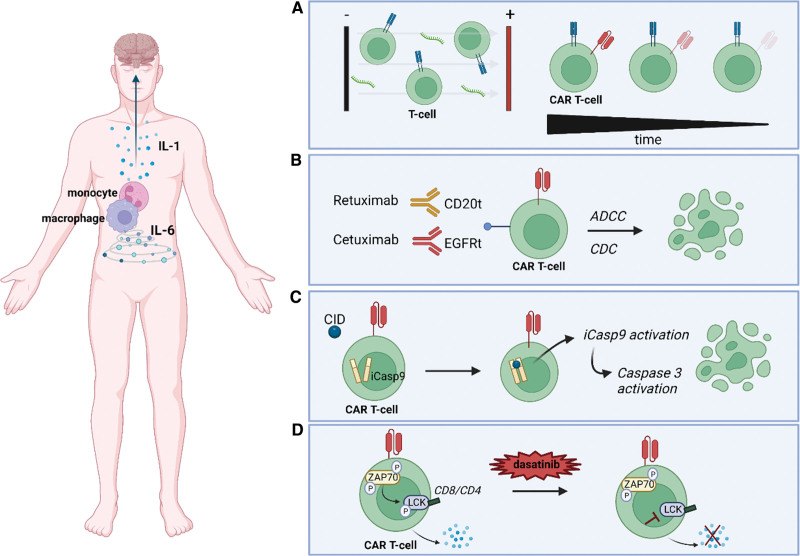
Figure 2.
Strategies to acquire control over the cytokine release of CAR-T cells. (A) mRNA electroporation, a nonviral transduction method resulting in CAR-T cells with transient activity to limit the risk of persistent toxicity. (B) ADCC or CDC of CAR-T cells containing a truncated CD20 (CD20t) or EGFRt molecule. (C) Suicide gene system consisting of iCasp9 activation after the administration of a CID, which will dimerize caspase 9 and subsequently activate the downstream executioner caspase 3, resulting in apoptosis of the CAR-T cell. (D) A temporary switch-off system using dasatinib to inhibit the phosphorylation of LCK, a key regulator for T-cell signaling. Created with BioRender.com. ADCC = antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; CAR = chimeric antigen receptor; CDC = complement-dependent cytotoxicity; CID = chemical inducer of dimerization; EGFRt = epidermal growth factor receptor; iCasp9 = inducible caspase 9; LCK = lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase.