Figure 2.
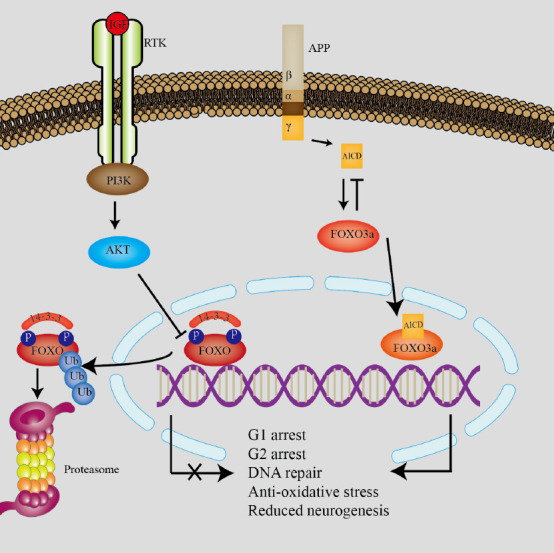
The classic insulin/IGF1/FOXO pathway and its association with APP.
The left signaling pathway shows the classic insulin/IGF1 (insulin-like growth factor 1)/FOXO (forkhead box protein O) pathway. In this pathway, insulin-stimulated cells activate Akt. Akt then phosphorylates and inactivates FOXO, resulting in translocation to the cytoplasm for degradation by ubiquitination. When FOXO is in the nucleus it mediates transcription of various target genes such as G1 arrest, G2 arrest, DNA repair, anti-oxidative stress, cell differentiation, and other effects in stem cells. The right signaling pathway shows that amyloid precursor protein (APP) may be involved in development of Alzheimer’s disease. The amyloid APP intracellular domain (AICD) is a byproduct of APP metabolism, produced by sequential proteolytic cleavage by α/β and γ-secretases. AICD activates FOXO3a resulting in reduced neurogenesis. Reduced neurogenesis may be a mechanisms of brain shrinkage in AD. Created with Adobe illustrator. FOXO: Forkhead box protein O; IGF1: insulin-like growth factor 1; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RTK: receptor tyrosine kinases.
