Figure 3.
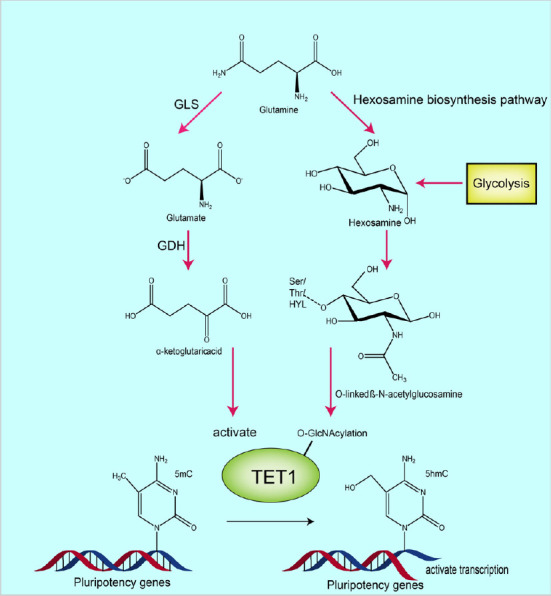
The underlying mechanisms by which glutamine metabolism and glycolysis promote TET1 catalysis under hypoxic conditions.
The process on the left shows that glutamine is converted to glutamate by glutaminase, then further converted to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) by glutamate dehydrogenase or transaminases (PSAT/GOT/GPT). Catalytic activity of TET1 is then increased by α-KG. The process on the right shows that glycolysis and glutamine can fuel the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway, the product of which is O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc), which is produced by O-GlcNAc transferase-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of TET1. This product positively regulates TET1 activity. Created with Adobe illustrator. GDH: Glutamate dehydrogenase; GLS: glutaminase; TET1: ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenase 1.
