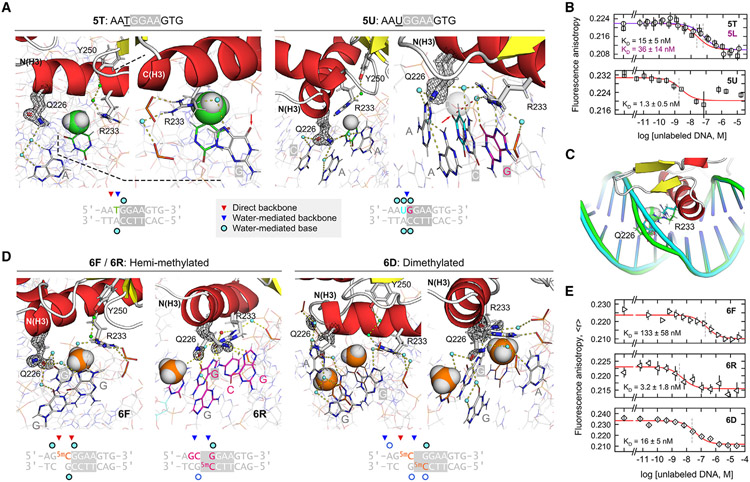
Figure 5. Control of PU.1/DNA binding in the 5'-flanking region: Importance of the Q226-R233 couple.
(A) Paired structures of two complexes in which a 5-methyl substituent of one (5T) sterically displaces the water-mediated linkage of Q226 and R233, and its non-methyl counterpart (5U). The 5-methyl of T−1 and H of U−1 are rendered as van der Waals (vDW)-sized spheres. In 5T, the arrow marks O6 of the core G0 residue, which is normally contacted by R233. In 5U, the arrow marks O8 of U−1, which H-bonds with the ordered water otherwise contacted by Q226 in high-affinity complexes.
(B) DNA binding by 5T, 5L, and 5U. Points represent mean ± SD of three technical replicates.
(C) Structural alignment of 5T and 5U showing the local deformation in DNA structure at the methylated position in 5T. See also Figure S7.
(D) Co-crystal structures of hemi- (6F and 6R) and dimethylated CpG variants (two views of 6D) of the high-affinity 1H complex. The 5-methyl groups in the 5mC residues are rendered as spheres.
(E) DNA binding of the CpG-methylated complexes. Points represent mean ± SD of three technical replicates.