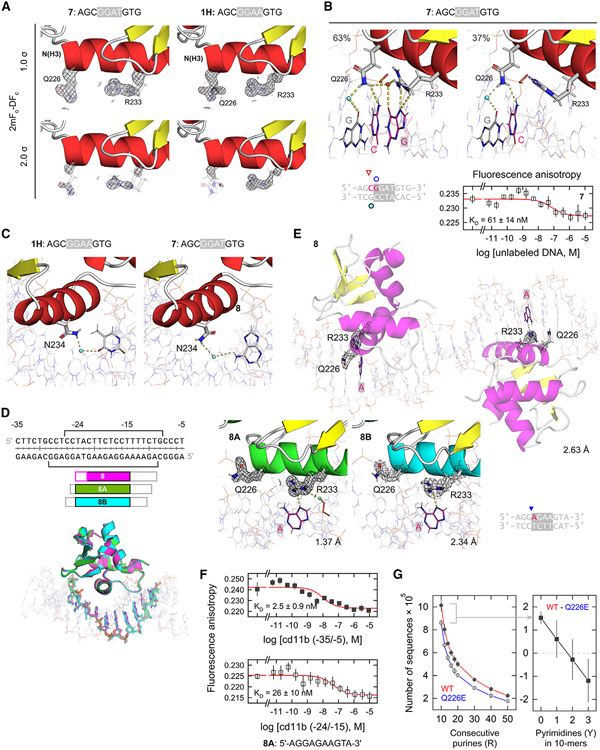
Figure 6. DNA complexes of PU.1 with non-canonical DNA sites.
(A) Comparison of the key residues Q226 and R233 in complex with the non-canonical sequence 5'-AGCGGATGTG-3' (7) and canonical 1H. The DNA and ordered hydration are omitted for clarity.
(B) DNA contacts by the two resolved occupancies by R233 in complex 7, together with its titration profile. Points represent mean ± SD of three technical replicates.
(C) N234 determines affinity but not specificity in DNA recognition by PU.1. N234 in both 1H and its 5'-GGAT-3' analog (7) contacts the complement of the altered base via an ordered water molecule, acting as a universal H-bonding adapter. It has also been shown that the point mutation N234A is sufficient to abolish high-affinity binding by PU.1.56
(D) The proximal fragment (−35/−5) of the CD11b promoter. Brackets indicate the reported DNase I footprints for PU.1.44 Co-crystal structures of ΔN165 bound with DNA sequences sampling various windows of the full CD11b fragment were aligned by the proteins. Alignment of the protein-bound DNA sequences reveals the target sequence −24/−15: AGGAGAAGTA. Open boxes correspond to non-CD11b bases derived from the cassette needed for crystallography. In the aligned complexes, only the purine-rich strand was colored for clarity. See also Table S3.
(E) The 8-series of CD11b complexes. 2mFo-DFc maps are rendered at the 1.0 σ level. Co-crystal 8 exhibits two complexes per asymmetric unit. The electron density Q226 in one of the 8 complexes is very low and, considering the flipped-out conformation in the other complex as well as co-crystals 8A and 8B, its conformation in that complex should be considered indeterminate.
(F) Titration profiles for the full CD11b promoter and the localized site centered between positions −24/−15. Points represent mean ± SD of three technical replicates.
(G) Preference for purine-rich genomic DNA by WT PU.1 over Q226E, which exhibits increased pyrimidine tolerance in terms of length of purine tracks (left) or pyrimidine content in 10-bp tracks. Points represent the mean ± SD of a bootstrapping procedure that randomly sampled 10% of the data.