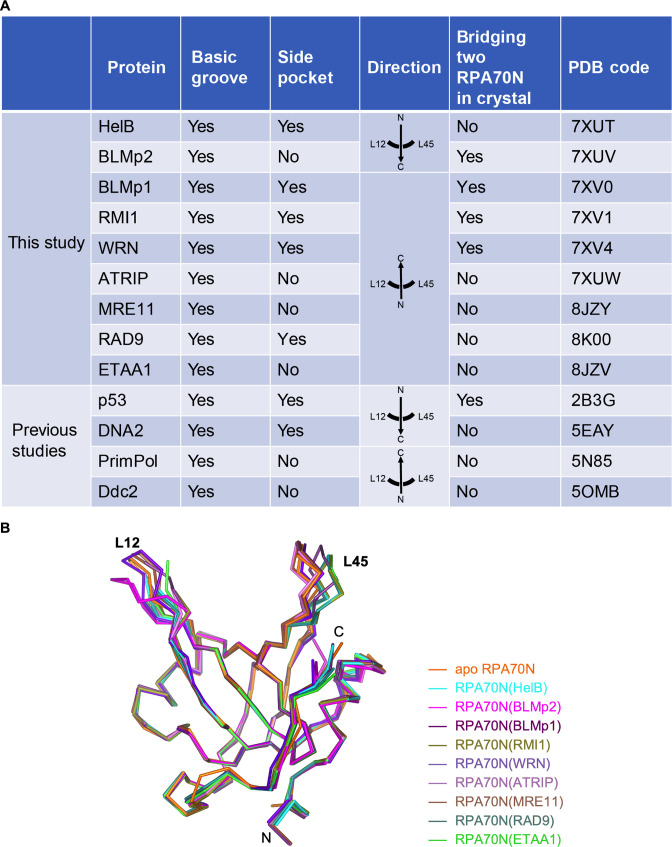
Figure 10. Comparison of RPA70N–peptide complex structures.
(A) Summary of the RPA70N-binding proteins for which RPA70N complex structures are available (Ddc2 binds to Rfa1N). (B) Superposition of apo RPA70N (orange, PDB: 2B29) with RPA70N structures determined in this study, colored using the peptide color code used in Figure 1F–N.