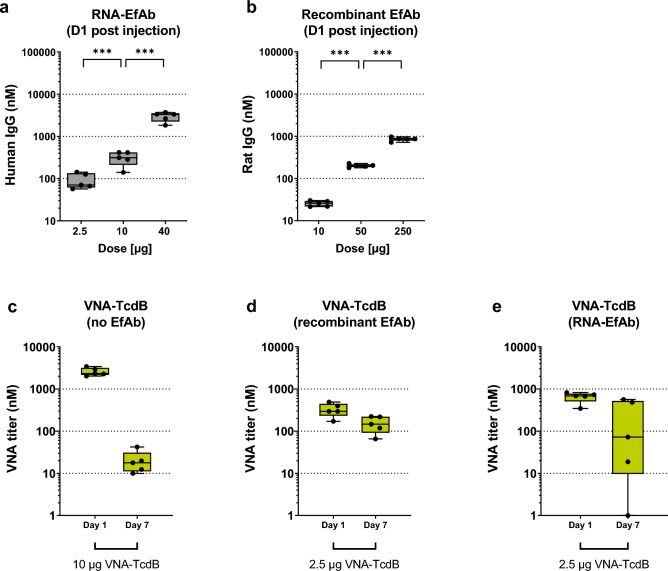
Figure 3.
Co-administration of EfAb enhances the half-life of VNAs in vivo. (a, b) Quantification of serum titer, one day following a single intravenous injection of various doses of mRNA-LNP encoding EfAb (a, Total human IgG ELISA, Supplement Table 2) or recombinant rat EfAb (b, rat EfAb ELISA, Supplement Table 2) in outbred CD-1 mice. Data is depicted as whisker plots showing min to max values of five individual mice. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (c) Quantification of serum VNA-TcdB titer (VHH detection ELISA, Supplement Table 2) at either Day 1 or Day 7 following a single intravenous injection of 10 µg of mRNA-LNP encoding VNA-TcdB in outbred CD-1 mice (same groups as shown in Fig. 2a). Data is depicted as whisker plots showing min to max values. For each timepoint, an independent cohort of five mice was used. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (d, e) Quantification of serum VNA-TcdB titer (VHH detection ELISA, Supplement Table 2) at either Day 1 or Day 7 following a single intravenous injection of 2.5 µg of mRNA-LNP encoding VNA-TcdB together with either 100 µg of co-administered recombinant rat EfAb (d) or 10 µg of mRNA-LNP encoded human EfAb (e) in CD-1 mice. Data is depicted as whisker plots showing min to max values. For each timepoint, an independent cohort of five mice was used.