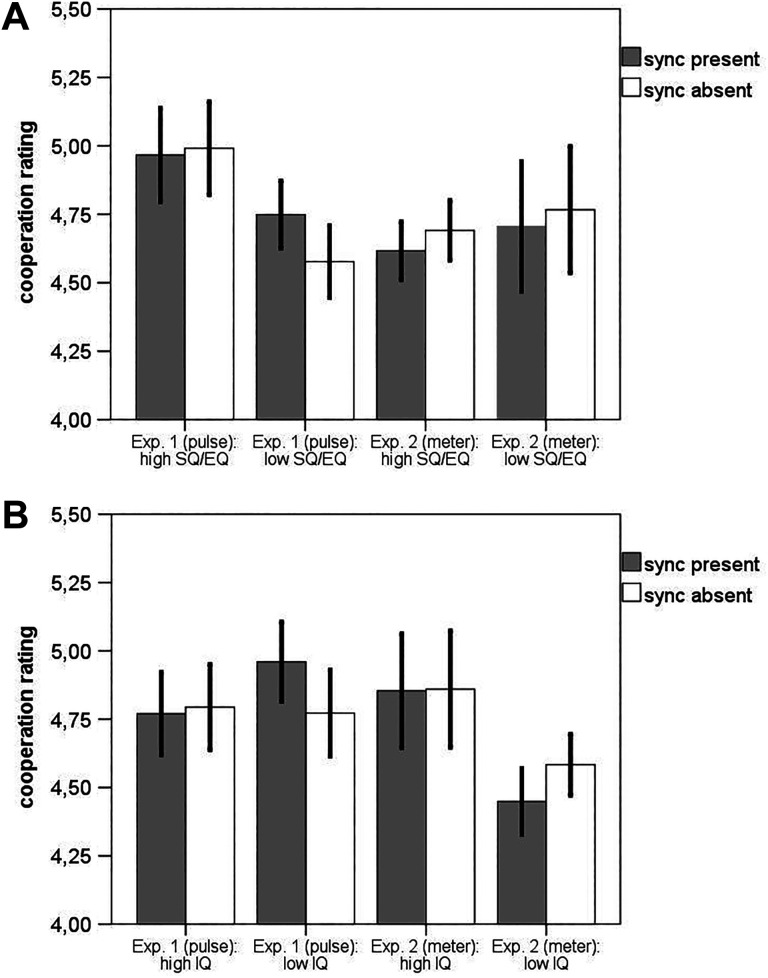
Figure 1.
(A) Cooperation ratings based on the median split of the systemizing quotient/empathy quotient (SQ/EQ) ratio values for individual participants. Gray columns display mean cooperation ratings averaged across participants for the trial pairs, in which both interacting agents exhibit the same pulse in utterances, and white columns display mean cooperation ratings averaged across participants for the trial pairs in which interacting agents exhibit different pulse. Error bars (uncorrected for the within-subject design) stand for ±2SE around the mean. The data showed that participants with higher SQ relative to EQ values are less sensitive to pulse synchronization as a signal of cooperation. However, this trend is not evident for the pairs of interacting agents with similar versus different meter. (B) Cooperation ratings based on the median split of the nonverbal IQ scores for individual participants. Gray columns display mean cooperation ratings averaged across participants for the trial pairs, in which both interacting agents exhibit the same pulse in utterances, and white columns display mean cooperation ratings averaged across participants for the trial pairs, in which interacting agents exhibit different pulse. Error bars (uncorrected for within-subject design) stand for ±2SE around the mean. The data showed that participants with lower nonverbal IQ are more sensitive to pulse synchronization as a signal of cooperation. However, this trend is not evident for the pairs of interacting agents with similar versus different meter.