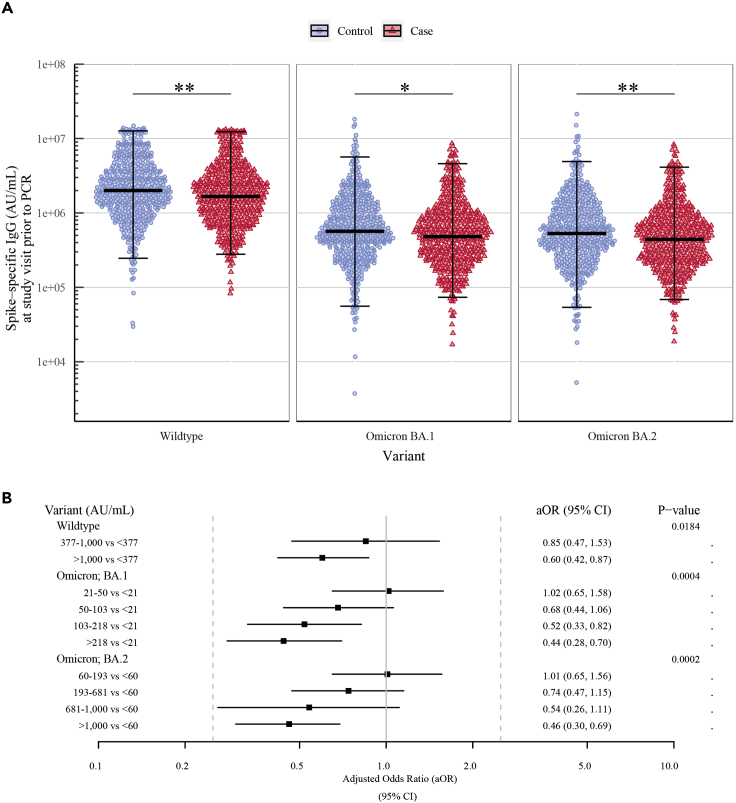
Figure 2.
High levels of spike-specific IgG and ACE2-blocking antibody titers were associated with lower odds of Omicron breakthrough infection
(A) Comparison of spike-specific IgG levels (AU/mL) quantified at a study visit prior to a positive (cases, n = 482) or negative PCR test (controls, n = 482) showing the geometric mean and 95% CI. SARS-CoV-2 variants from left to right: Wildtype (Wuhan-Hu-1), Omicron BA.1, and Omicron BA.2. ∗ = p ≤ 0.05 and ∗∗ = p < 0.01.
(B) Multivariable logistic regression showing the adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% CI for breakthrough infection for ACE2-blocking antibody titers in tertiles (wildtype) or quintiles (Omicron variants). The analysis adjusts for the matched variables: age group, sex, vaccine, and study visit, and for the unmatched variables: vaccine priority group, Charlson comorbidity index (CCI), visit year, days from study visit to PCR test, and days from third vaccination to PCR test.