Fig. 1.
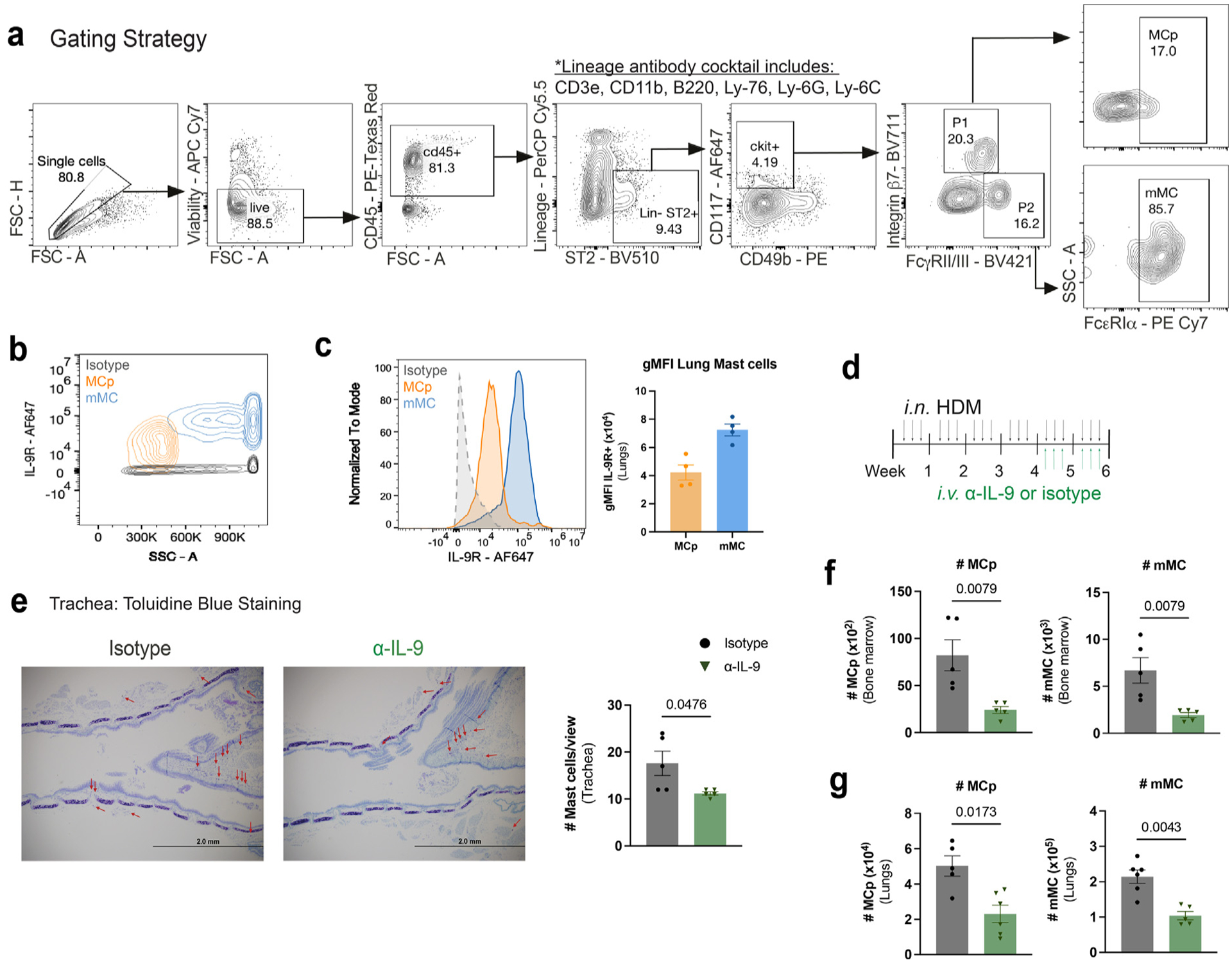
MCp and mMCs are IL-9 responders in the allergic lung. (A) Flow cytometry MC gating strategy using representative flow cytometry plots. P1 and P2 are further gated on FcεRIα+ cells. Mast cell progenitors (MCp) and mature mast cells (mMC). (B–C) Naïve WT lung MC were analyzed using flow cytometry for IL-9 receptor expression: B, representative flow cytometry contour plot of IL-9R expression on MC. (C) Histogram for IL-9R and geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) for each population was compared to isotype control (n = 3–4). (D–G) HDM-treated WT mice were treated with α-IL-9 or isotype control during the last 2 weeks of HDM treatment. (D) Schematic of experimental design. (E) MC numbers and frequencies were assessed in the trachea via toluidine blue staining; F–G: flow cytometry analysis of bone marrow (F) and lung (G) MC (n = 5–6) Data are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. Error bars indicate ± standard error of mean. Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparisons to generate p values in (C) and (E–G). APC = Allophycocyanin; CD=clusters of differentiation; FSC = forward scatter; HDM = house dust mite; IL = interleukin; MC = mast cell; MCp = MC progenitors; mMC = mature MC.
