Fig. 3.
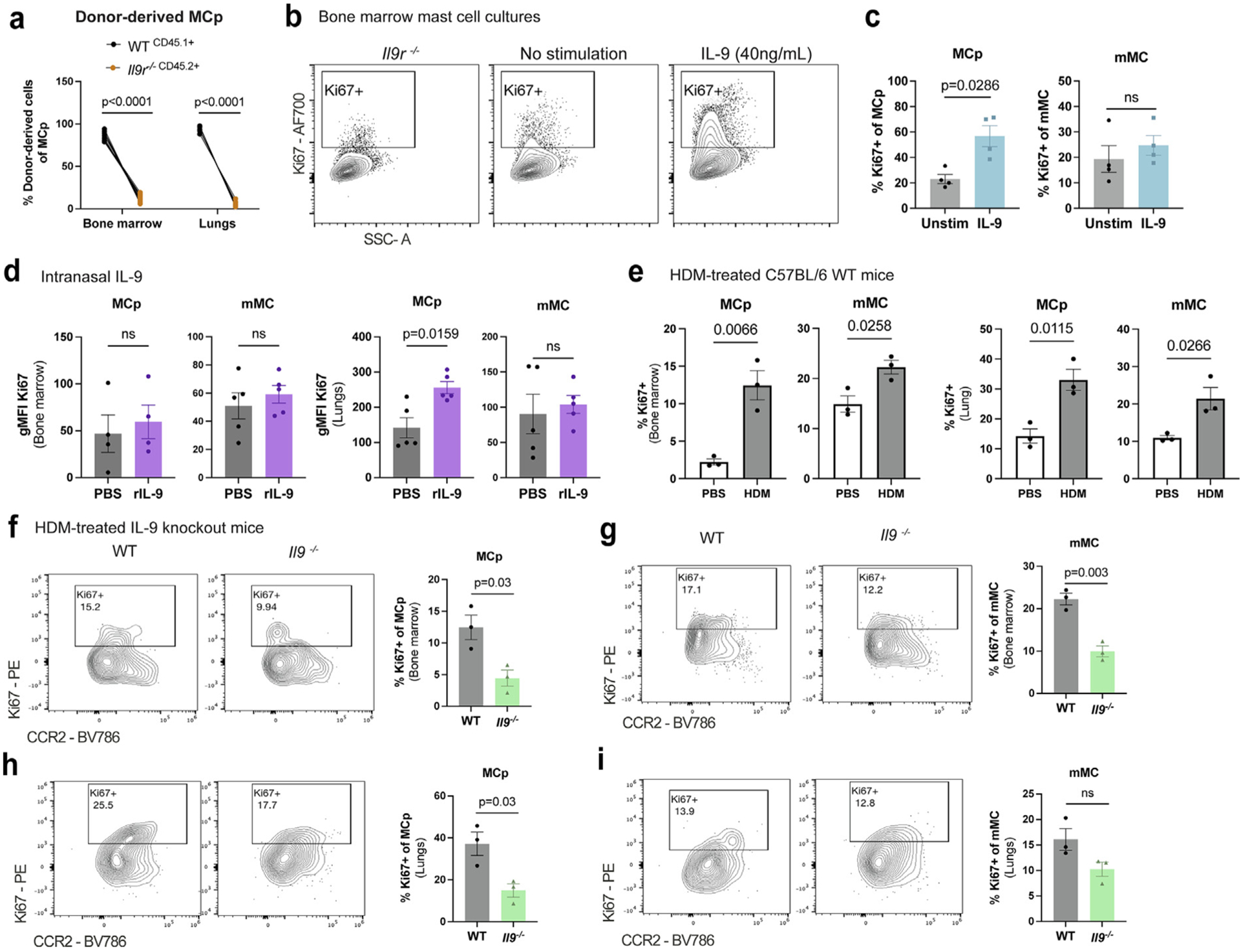
IL-9 enhances MC progenitor proliferative capacity. (A) WT (CD45.1+) and Il9r−/− (CD45.2+) bone marrow cells were transferred to lethally irradiated Boy/J x C57BL/6J F1 mice and after 3 months to allow repopulation of the immune system, mice were treated with HDM for 6 weeks. Flow cytometry analysis of CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ of lung MCp. (n = 10). (B–C) BMMC from WT mice were cultured for 2 weeks in IL-3 and SCF in RPMI. BMMC were harvested and stimulated with IL-9 (40 ng/ml) for 2 hours to assess intracellular Ki67 using flow cytometry. (B) flow cytometry plots of Ki67 staining in BMMC with WT and Il9r−/− BMMC. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of Ki67 frequencies in MCp and mMC (n = 4). (D) WT mice were intranasally treated with rIL-9 for 3 days. Flow cytometry of Ki67 gMFI was measured from bone marrow and lung MC (n = 5); E, flow cytometry analysis of Ki67 was assessed in lung MC from 6-week HDM-treated WT mice or PBS controls (n = 3). (F–I) Il9−/− and WT mice were treated intranasally with HDM 3x/week for 6 weeks. Ki67 expression was assessed via flow cytometry in (F–G) bone marrow and (H–I) lung MC (n = 3). Each data point represents an individual mouse. Data are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. Error bars indicate ± standard error of mean. Statistical significance was determined by analysis of variance, followed by Sidak’s multiple comparison test (A), Mann-Whitney U test (C–D), and Student’s t test (E–I). CD = clusters of differentiation; gMFI = geometric mean fluorescence intensity; HDM = house dust mite; IL = interleukin; MC = mast cell; MCp = MC progenitors; mMC = mature MC; ns = not significant; PBS = phosphate buffered saline; PE = R-phycoerythrin; r = recombinant; SSC = side scatter; WT, wild type.
