Figure 3.
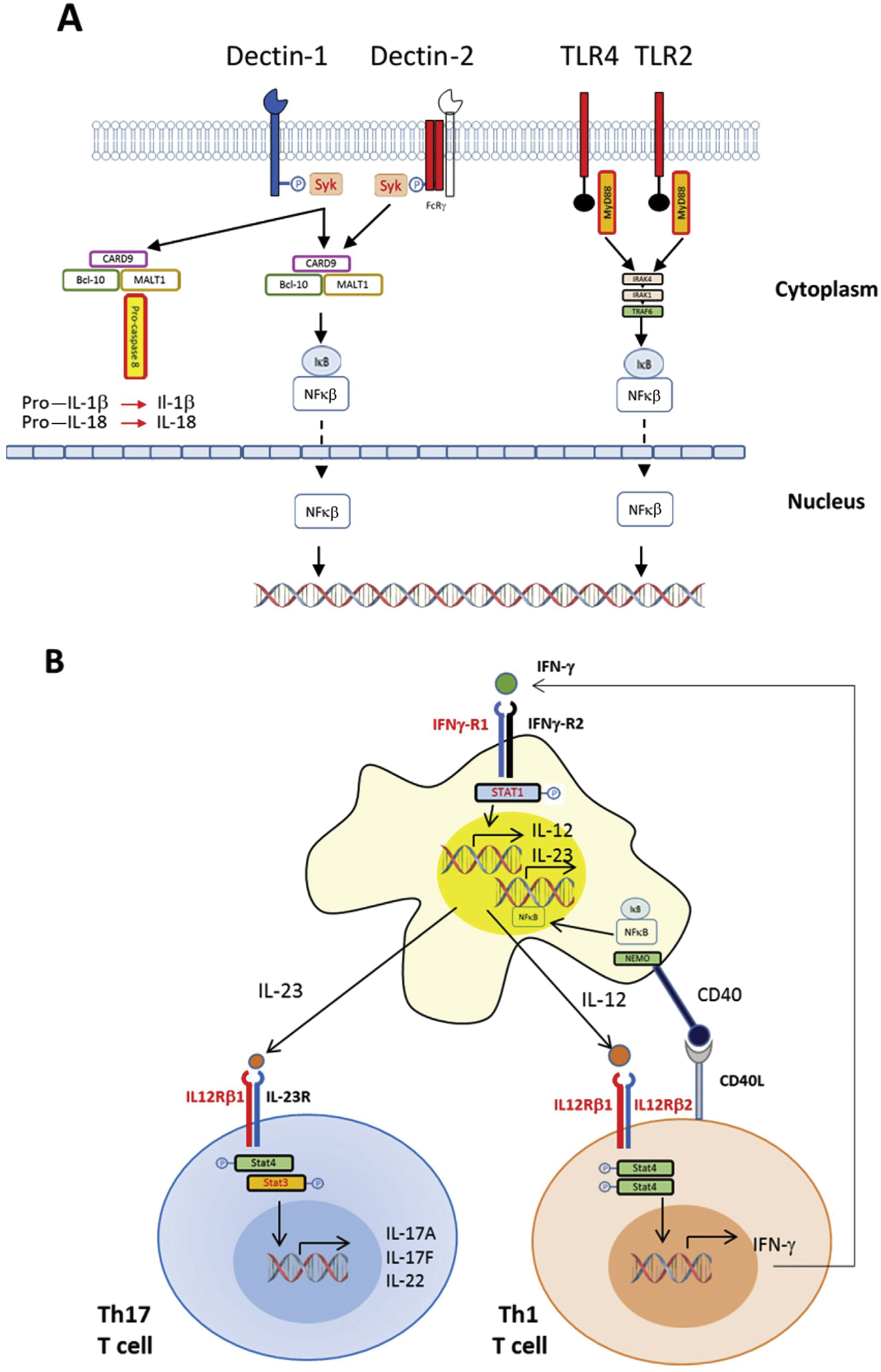
Immunobiology of coccidioidomycosis. (A) This simplified diagram outlines the recognition of fungal pathogen–associated molecular patterns by pattern recognition receptors that trigger activation of macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells. Dectin-1 and Dectin-2 are examples of C-type lectin receptors involved in recognition of fungal cell wall components. Aggregation of Dectin-1 molecules in the presence of fungal polysaccharide ligands triggers phosphorylation of its cytoplasmic tail, leading to activation of Syk kinase, which induces formation of the CARD9-Bcl10-Malt1 complex, which mediates activation of nuclear factor kappa β (NF-κβ) and the production of cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-12, that activate and promote differentiation of T cells. Malt-1 can also engage and proteolytically cleave pro-caspase 8, activating the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18. Recognition of coccidioidal molecules by Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) is essential for vaccine-induced protection in murine models of coccidioidomycosis. Homodimers or heterodimers containing TLR2 are linked by an adaptor molecule to MyD88, activating IRAK4; subsequent downstream signaling leads to degradation of the IkB complex, releasing NF-κB complexes and allowing their nuclear entry and activation of cytokine transcription. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and Dectin-2 have not been confirmed to play a role in coccidioidomycosis but are important in other mycoses. (B) Differentiation of CD4 T cells and their polarization into Th1 or Th17 cells and crosstalk with macrophages and other antigen-presenting cells. As outlined in panel A, recognition of fungal cellular components leads to activation of macrophages and other phagocytes, which release IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-23, and other cytokines that promote the expansion and differentiation of naive CD4 T cells. Those that become Th17 cells express IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22, which promote production of antimicrobial peptides in epithelial cells. CD4 T cells that differentiate along the Th1 pathway in response to IL-12 release interferon gamma (IFN-γ), which enhances phagocytosis by macrophages and other phagocytes and the release of antimicrobial molecules. Red lettering reveals receptor and signaling molecules in which deleterious mutations have been found in cases of disseminated coccidioidomycosis.33,35,91 STAT = signal transducer and activator of transcription.
