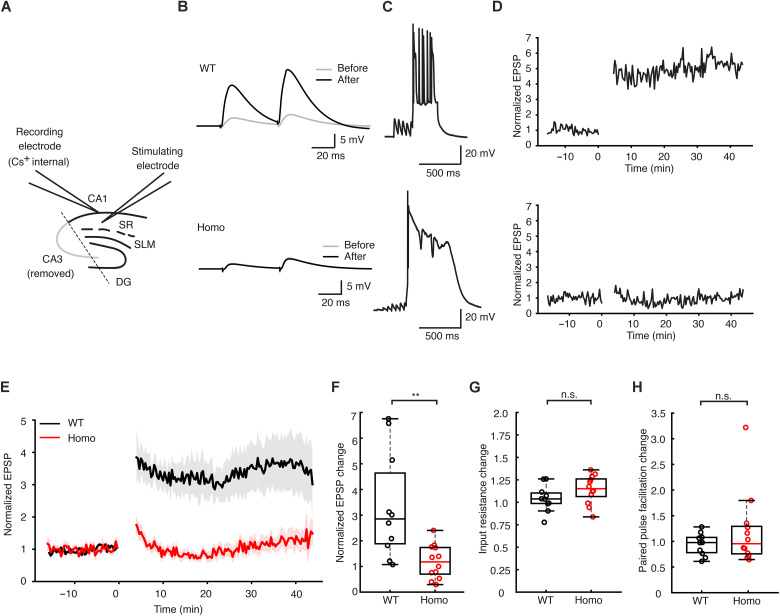
Fig. 4. Reduced BTSP in CaMKII T286A homozygous mutant mice in slice experiments.
(A) Schematic of the slice experiment, with excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) elicited by electrical stimulation in the stratum radiatum (SR) area of the hippocampus; SLM, stratum lacunosum-moleculare; DG, dentate gyrus. CA3 region was removed to prevent excessive input from CA3 neurons interfering with recordings. (B) Example raw traces of EPSPs before and after BTSP induction in the WT group (top) and in the Homo group (bottom). (C) Example traces during the BTSP inductions from the WT group (top) and the Homo group (bottom). (D) EPSP amplitude plotted against time, with cells recorded for over 15 min before induction to ensure stable baselines. Postinduction recordings last up to 40 min. (E) Group data for EPSP amplitude plotted against time, with lines and shaded backgrounds representing means ± SEM, respectively. (F) Quantification of the EPSP amplitude change. The change is calculated by dividing the averaged EPSP amplitude before induction from the EPSP amplitude after induction in each of the cells. T = 3.39, P = 0.00291. (G) Quantification of the changed input resistance (before and after induction) of the WT and homozygous groups. T = −1.52, P = 0.144. (H) Quantification of the changed paired-pulse facilitation rate (before and after induction) of the WT and homozygous groups. The paired-pulse facilitation rate was calculated by dividing the first EPSP’s amplitude from the second EPSP’s amplitude. Z = −0.528, P = 0.598 (rank sum test). Statistical analyses used two-sample Student’s t test for parametric tests and Wilcoxon rank sum test for nonparametric test. **P < 0.01; n.s. (P ≥ 0.05). Sample sizes: n = 10 (WT) from eight mice and n = 12 (Homo) from five mice.