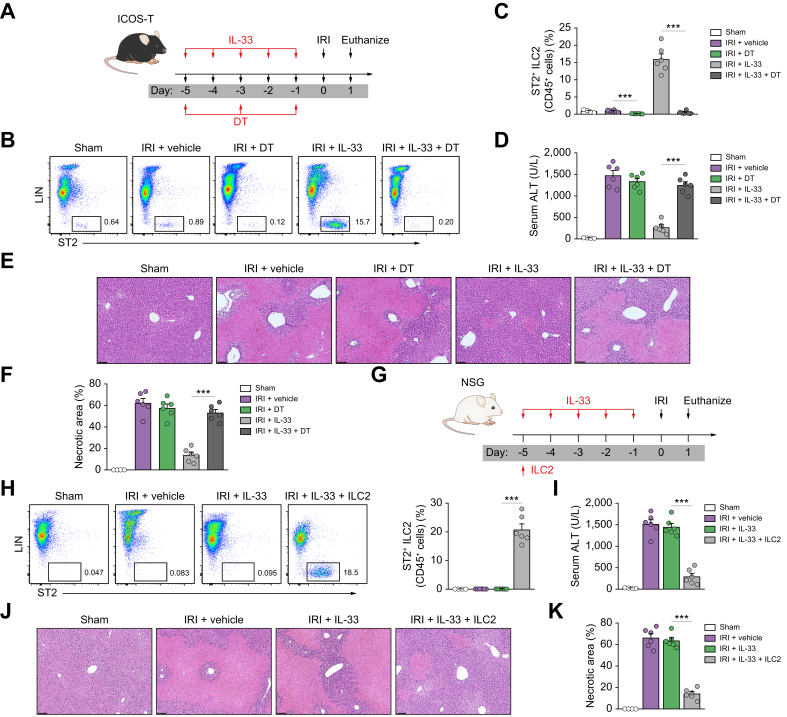
Fig. 4.
ILC2 played a key role in IL-33-mediated hepatoprotection in IRI mice.
(A) ICOS-T C57BL/6 mice were treated with mouse recombinant IL-33 daily for 5 consecutive days, as well as DT at Days -5, -3, and -1 before hepatic ischaemia. (B and C) Percentage of ST2+ ILC2 in the CD45+ leucocyte compartment from the livers of sham, IRI + vehicle, IRI + DT, IRI + IL-33, or IRI + IL-33 + DT mice. (D) Representative H&E-stained sections of livers from mice 1 day after IRI. Bar = 200 μm. (E and F) Liver necrosis areas and serum ALT levels were assessed in these mice. (G) NSG mice were injected with ILC2s isolated from BALB/c mice at Day -5 before ischaemia and were administered mouse recombinant IL-33 daily for 5 consecutive days. (H and I) Percentage of ST2+ ILC2 in the CD45+ leucocyte compartment from the livers of mice. (J) Representative H&E-stained sections of livers from mice 1 day after IRI. Bar = 200 μm. (K and L) Liver necrosis areas and serum ALT levels were assessed in these mice. Data shown are the mean ± SEM (n = 4–6 per group). Statistical significance was assessed using a one-way ANOVA. ∗∗∗p <0.001. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; DT, diphtheria toxin; ICL2, type 2 innate lymphoid cell; IRI, ischaemia/reperfusion injury; NSG, NOD-scid IL2rγnull.