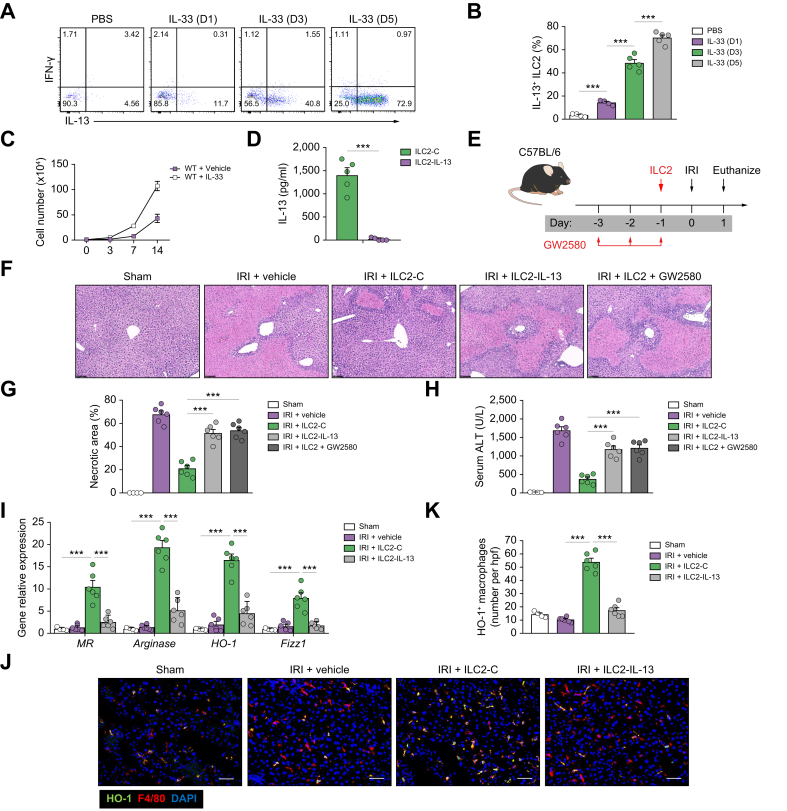
Fig. 5.
ILC2s protected against hepatic IRI through IL-13 production and induction of anti-inflammatory macrophages.
(A and B) Intracellular staining shows ILC2s harvested from livers at the specified time points after daily injections of IL-33 produce high levels of IL-13 and minimal amounts of IFN-γ. (A) Contains representative flow dot plots, and (B) shows percent of ILC2s expressing IL-13. (C) Liver ILC2 were isolated from C57BL/6 mice treated with or without IL-33 and cultured with IL-2, IL-7, and IL-33 for 14 days. The number of ILC2s was calculated at Days 3, 7, and 14. (D) ILC2s were transfected with control (ILC2-C) or IL-13 CRISPR-Cas9 (ILC2–IL-13). IL-13 was measured in culture supernatant of ILC2-C and ILC2–IL-13 via ELISA. (E) C57BL/6 mice were treated with transfected ILC2 1 day before ischaemia and with GW2580 daily for 3 consecutive days before ischaemia. (F) Representative H&E-stained sections of livers from mice 1 day after IRI. Bar = 200 μm. (G and H) Liver necrosis areas and serum ALT levels were assessed in these mice. (I) The mRNA expression of MR, arginase, HO-1, and FIZZ1 was quantified by qPCR in F4/80+ liver macrophages. (J and K) The numbers of HO-1+F4/80+ macrophages were assessed by immunofluorescence staining in liver sections. Bar = 100 μm. Data shown are the mean ± SEM (n = 4–6 per group). Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t test or ANOVA. ∗∗∗p <0.001. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HO-1, haem oxygenase-1; hpf, high-power field; ICL2, type 2 innate lymphoid cell; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IRI, ischaemia/reperfusion injury; qPCR, quantitative PCR; MR, mannose receptor; WT, wild-type.