Fig. 1.
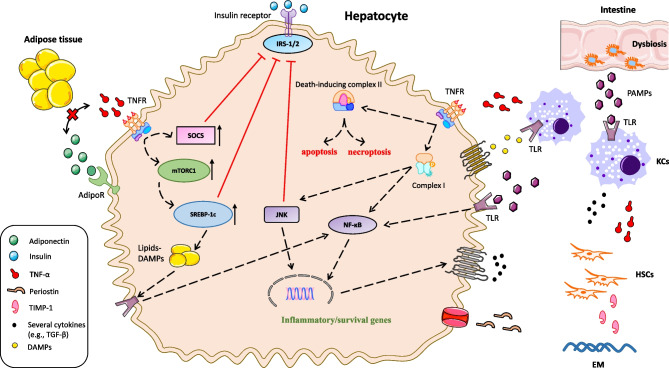
The role of TNF-α in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. In the liver, TNF-α is primarily produced by the KCs, which respond to two types of stimuli: the DAMPs, which are released by lipid-infiltrated and damaged hepatocytes, and the gut-derived PAMPs, which translocate from the intestine to the liver, due to an impaired intestinal epithelial barrier. Both DAMPs and PAMPs bind TLRs on the surface of the KCs and activate the NF-κB, which is the key signaling pathway for the transcription of TNF-α. Furthermore, fat-stressed hepatocytes also contribute to TNF-α production via the interaction between DAMPs/PAMPs and TLRs, albeit to a lesser extent. Once released, TNF-α binds TNFR and stimulates the assembly of complex I, which initiates two important downstream signaling pathways, i.e., the JNK and NF-κB pathways, through which TNF-α induces the transcription of target genes involved in inflammation, cell proliferation, and survival. Besides these cellular responses, TNF-α also induces cell death by enabling the assembly of the death-inducing protein complex II, leading to either apoptosis or necroptosis. Besides, inflammation, survival, and apoptosis, TNF-α also contributes to IR and NAFL development; TNF-α perpetuates IR in hepatocytes as it blocks insulin signaling at the post-receptor level; TNF-α triggers the expression of SOCS, which prevent tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and IRS-2 and promote their early degradation. Likewise, TNF-α-mediated activation of JNK contributes to the phosphorylation of serine of IRS-1 and IRS-2, which inhibits their signaling. In addition, TNF-α is proposed as a potential positive regulator of the mTORC1 pathway in the hepatocytes, inducing the expression of the SREBP-1c, the main transcription factor of de novo lipogenesis. TNF-α-induced SREBP-1c, in addition to promoting de novo lipogenesis, also suppresses the IRS-1/2 synthesis, thus contributing to IR. Notably, TNF-α also antagonizes adiponectin and suppresses its insulin-sensitizing effect on the hepatocytes. Finally, TNF-α is involved in hepatic fibrogenesis; TNF-α induces the production of TGF-β by the hepatocytes and KCs, upregulates the expression of periostin in the hepatocytes and TIMP-1 in HSCs, which facilitate collagen deposition and EM stabilization