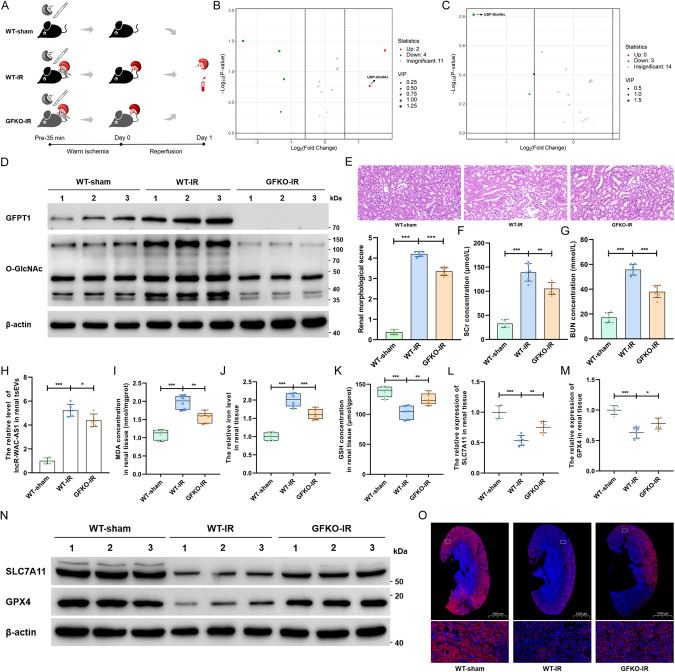
Fig. 3. GFPT1-mediated HBP metabolic acceleration suppresses SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression and promotes ferroptosis in mouse renal IRI model.
A Schematic representing in situ kidney warm ischemia-reperfusion injury protocol in WT and GFPT1 global knockout C57BL/6 mice. B Volcano plot illustrated all detected glucose metabolism-related metabolites in renal tissues of mice in WT-sham and WT-IR groups (n = 6 group−1). The red dots represent the prominently upregulated metabolites in the WT-IR group; green dots represent the considerably downregulated metabolites, and gray dots indicate no significant differences. C Volcano plot showing all detected glucose metabolites in WT-IR and GFKO-IR groups (n = 6 group−1). The green dots represent the significantly downregulated metabolites in GFKO-IR group. D IB assays examined the expression of GFPT1 and O-GlcNAc in renal tissues of WT and GFKO mice before and after IRI treatment. E HE staining (top) and renal pathological score (bottom) of renal tissue slice (n = 6 group−1); scale bar: 20 μm; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. The SCr (F) and BUN (G) concentrations of mice following different administrations (n = 6 group−1); one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. H The lncRNA-WAC-AS1 level in renal-derived tsEVs was normalized according to the level of WT-sham (n = 6 group−1); one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. MDA concentration (I), iron level (J) and GSH concentration (K) in renal tissues were normalized according to the level of WT-sham (n = 6 group−1); one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. The transcriptional (L, M) and translational (N) levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4 in renal tissues (n = 6 group−1); one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. O IF assays determining the expression level and region of SLC7A11 (red) in renal tissue slices; scale bar: 1000 μm for the 1X and 20 μm for the 400X. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, and *p < 0.05 represent significant differences between two groups.