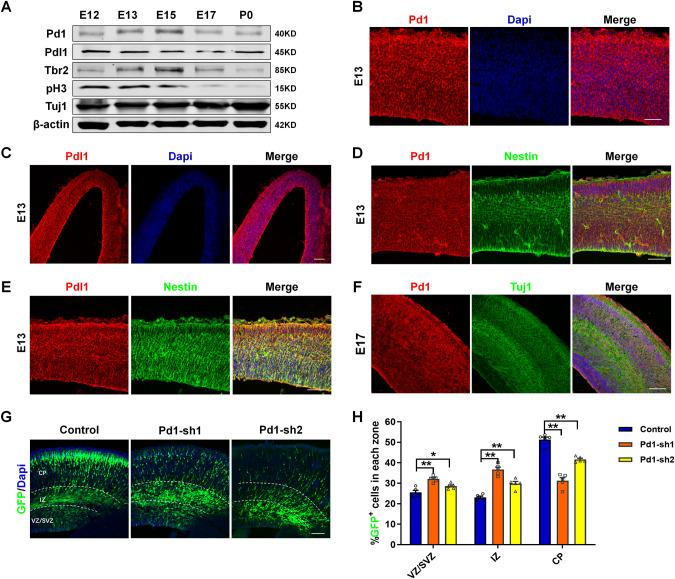
Fig. 1. Pd1 is expressed in the embryonic brain and involves in the regulation of neurogenesis.
A Western blot analysis shows Pd1 is expressed in the development of the cerebral cortex. Brains at E12, E13, E15, E17, and P0 were collected and subjected to western blotting. Lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies for Pd1, Pdl1, Tbr2, pH3, Tuj1, and β-actin. n = 3 individual experiments. B Images of E13 embryonic mouse brain sections stained for Pd1 and Dapi. n = 5 individual experiments. C Images of E13 embryonic mouse brain sections stained for Pdl1 and Dapi. n = 5 individual experiments. D Pd1 is co-labeled with Nestin at E13. n = 5 individual experiments. E Pdl1 is co-labeled with Nestin at E13. n = 5 individual experiments. F Pd1 is expressed in the membrane of neurons labeled with Tuj1 at E17. n = 5 individual experiments. G Pd1 knockdown causes abnormal GFP+ cell distribution in the developing neocortex. Control, Pd1-sh1, and Pd1-sh2 plasmids were electroporated into the embryonic brain at E13. The brains were harvested at E16 and then sliced into sections for analysis. H Graph shows the percentage of GFP+ cells in the VZ/SVZ, IZ, and CP. VZ/SVZ ventricular zone/subventricular zone, IZ intermediate zone, CP cortical plate. Error bars represent means ± S.E.M.; Two-tailed unpaired t-test, P < 0.05(*), P < 0.01(**), n.s. not significant. The scale bar represents 100 μm.