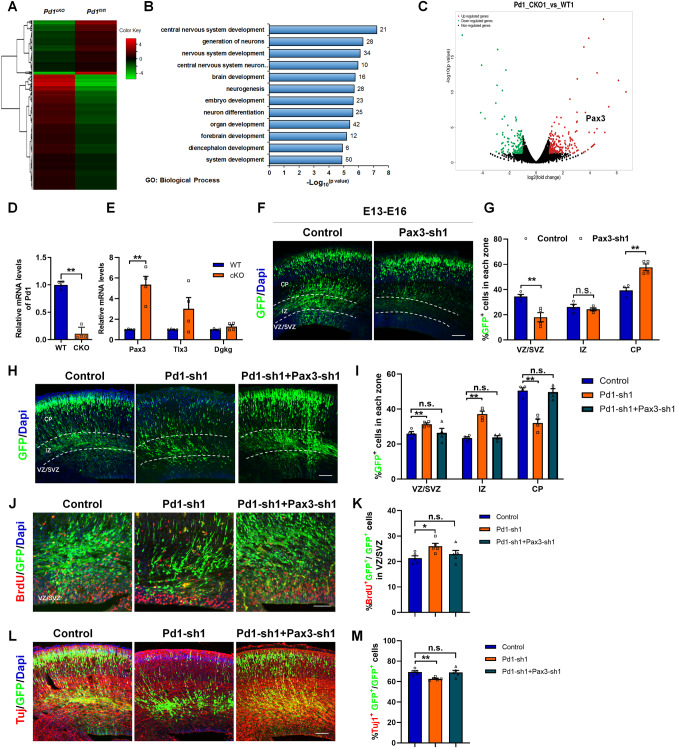
Fig. 5. Pd1 regulates embryonic neurogenesis by targeting Pax3.
A Pd1 deletion results in global gene expression variation. Hierarchical clustering analysis of genes that change fold is more than two between Pd1fl/fl mice and Pd1cKO mice. B Gene ontology analysis of dysregulated genes in Pd1cKO mice brains. C Image of Volcano plots shows the downregulated (green) and upregulated genes (red). D The mRNA level of Pd1 is obviously reduced upon Pd1 deletion. n = 4 individual experiments and p = 0.00001. E Loss of Pd1 results in an obvious increase in the expression of Pax3. n = 4 individual experiments and p = 0.002 for Pax3; p = 0.116 for Tlx3; p = 0.172 for Dgkg. F Downregulation of Pax3 leads to abnormal cell distribution in brain development. The plasmid of control and Pax3-sh1 were electroporated into the embryonic brain respectively at E13 and collected at E16 for further analysis. G Percentage of GFP+ cells in each zone of the cerebral cortex. n = 4 mice, p = 0.007 for VZ/SVZ; p = 0.468 for IZ; p = 0.002 for CP. H Abnormal cell distribution caused by Pd1 downregulation is partially rescued by Pax3-shRNA. I Graph shows the percentage of GFP+ cells in each zone. p = 4 mice, p = 0.009 (Control&Pd1-sh1) and p = 0.889 (Control&Pd1-sh1+Pax3-sh1) for VZ/SVZ; p = 0.0003 (Control&Pd1-sh1) and p = 0.726 (Control&Pd1-sh1+Pax3-sh1) for IZ; p = 0.0005 (Control&Pd1-sh1) and p = 0.753 (Control&Pd1-sh1+Pax3-sh1) for CP. J BrdU incorporation defects induced by Pd1 knockdown are rescued by Pax3 suppression. K Graph shows the percentage of BrdU incorporation in GFP+ cells in VZ/SVZ. n = 5 mice, p = 0.014 for Control&Pd1-sh1; p = 0.383 for Control&Pd1-sh1+Pax3-sh1. L Downregulation of Pax3 overrides neuronal differentiation defects caused by Pd1 knockdown. M Graph shows the percentage of Tuj1+GFP+ cells relative to all GFP+ cells. n = 5 mice, p = 0.002 for Control&Pd1-sh1; p = 0.884 for Control&Pd1-sh1+Pax3-sh1. Error bars represent means ± S.E.M.; Two-tailed unpaired t-test, P < 0.05(*), P < 0.01(**), n.s. not significant. The scale bar represents 100 μm.