Fig. 3. Genes at OOA-specific risk loci for mood disorders interact with neuropsychiatry-related gene networks.
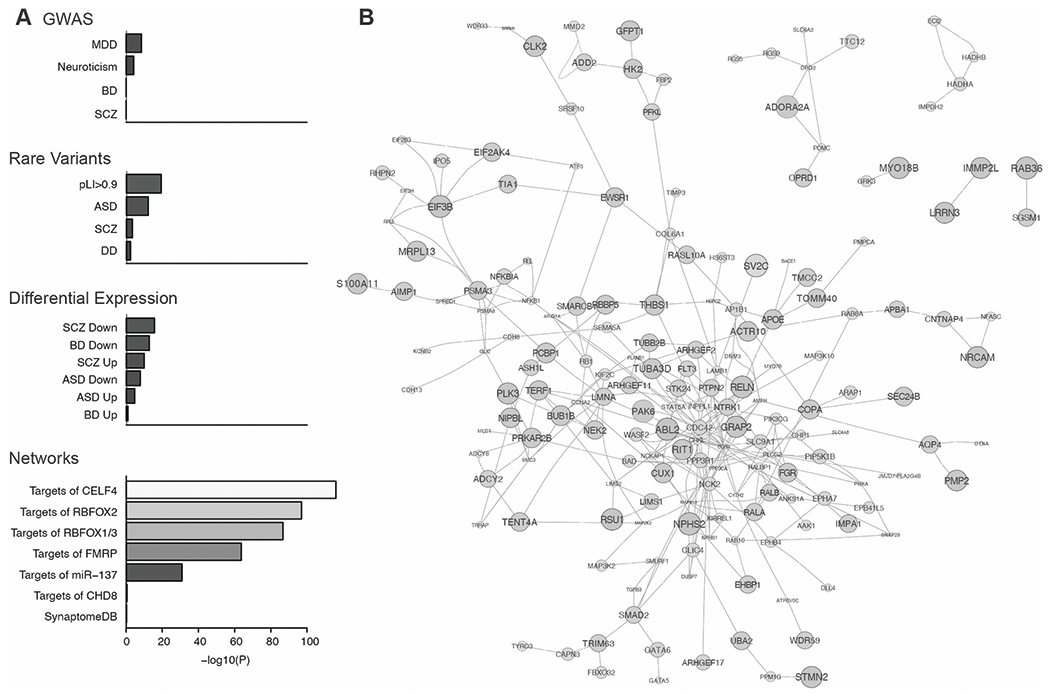
A Putative OOA risk genes (820 genes; MAGMA, P < 0.01) had an elevated rate of protein-protein interactions with gene sets derived from GWAS, rare variant studies, differential gene expression, and network analyses of psychiatric disorders. B Protein-protein interactions among the top 250 genes at OOA risk loci prioritized by their centrality in a gene network centered on known neuropsychiatry-related genes and strength of their statistical association with mood disorders in the OOA. Larger node size corresponds to more significant MAGMA p values.
