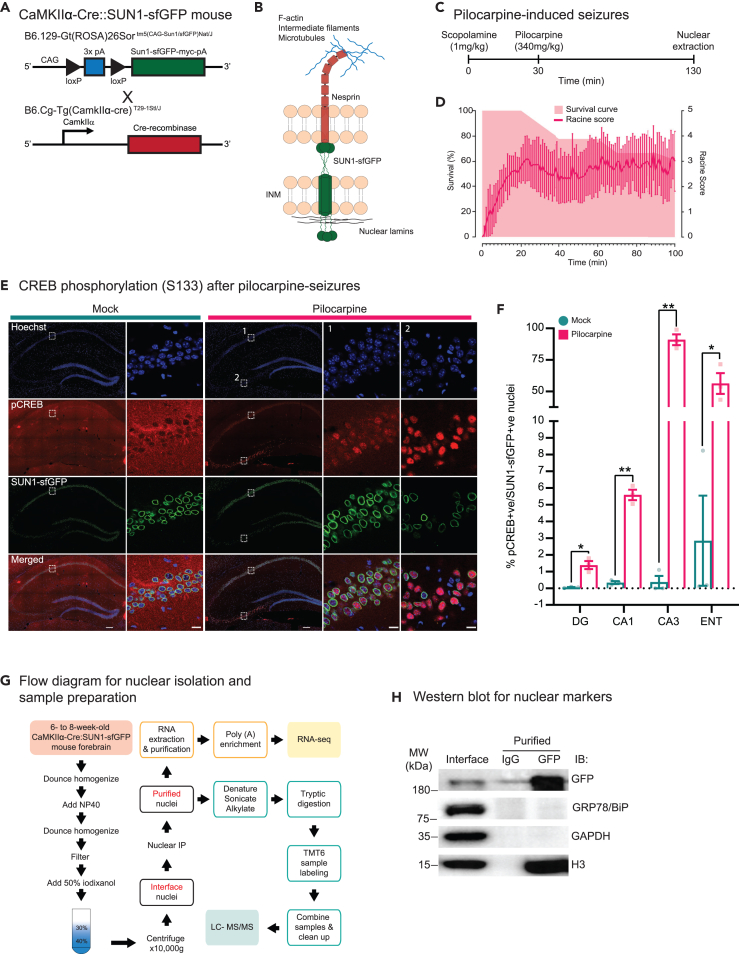
Figure 1.
Pilocarpine-induced seizures of CaMKIIα-Cre:SUN1-sfGFP mice
(A) Transgenic mice used in the study and breeding plan for CaMKIIα-Cre:SUN1-sfGFP.
(B) Localization of SUN1-sfGFP and nesprin in nuclear membrane and their association with cytoskeletal elements in the nuclear periphery.
(C) Timeline of seizure induction by intraperitoneal administration of scopolamine and pilocarpine.
(D) Survival curve of pilocarpine-injected CaMKIIα-Cre:SUN1-sfGFP mice over the duration of the experiment. Seizure behaviors were video recorded and scored based on the Racine scale.
(E) Immunohistochemistry showing pCREB (S133) expression in CA1 (ROI#1) and CA3 (ROI#2) regions of the hippocampus in mock and pilocarpine-injected mice. SUN1-sfGFP (green); Hoechst (blue); pCREBS133 (red). Scale bars, 200 μm; 10 μm (magnified).
(F) Quantification of SUN1-sfGFP-positive and pCREB-positive neuronal nuclei (N = 3 pairs of animals; Total number of cells quantified = 14816 (mock)/12676 (pilocarpine) [DG], 2746 (mock)/2964 (pilocarpine) [CA1], 265 (mock)/276 (pilocarpine) [CA3], 3256 (mock)/3090 (pilocarpine) [ENT]. Paired t test with means ± SEM, p < 0.05 (∗), p < 0.01 (∗∗).
(G) Diagram of the nuclear isolation from the mouse forebrain.
(H) Western blot of nuclear extracts from interface stage and after purification with anti-GFP antibodies. Blots were labeled with antibodies against GFP, histone 3 (H3), GRP78/BiP, and GAPDH. IgG, Immunoglobulin G.