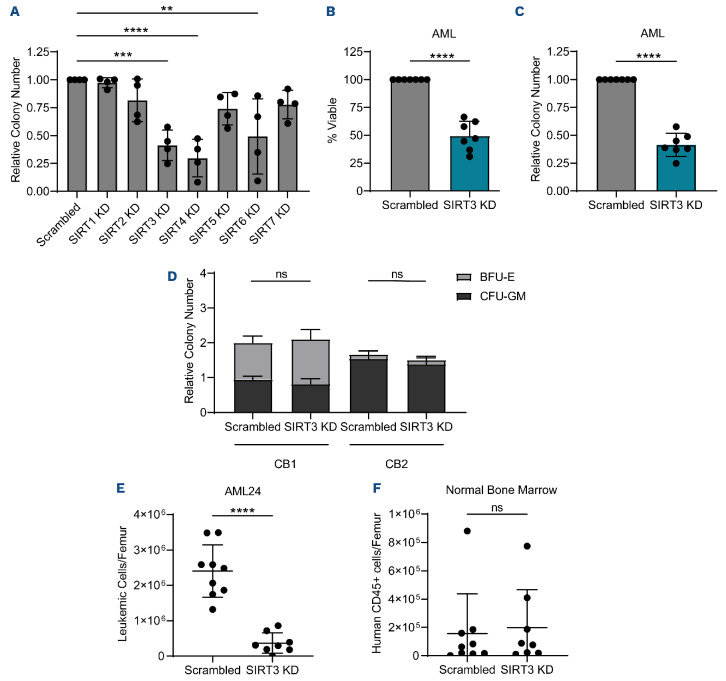
Figure 1.
SIRT3 knockdown targets acute myeloid leukemia but not hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. (A) Colony-forming ability of four primary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) specimens (AML1-4) post scrambled and sirturin (SIRT) targeting small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection. Colony-forming unit (CFU) assay was prepared immediately after electroporation. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA analysis. Each dot represents a primary AML specimen. (B) Viability of bulk AML 48 hours post scrambled or SIRT3 targeting siRNA transfection in 7 primary AML specimens (AML 1-5, 14 and 15). Statistical significance was determined using a paired t-test. Each dot represents a primary AML specimen. (C) Colony-forming potential of bulk AML post scrambled or SIRT3 targeting siRNA transfection in 7 primary AML specimens (AML. 1-5, 14, and 15). CFU assay was prepared immediately after electroporation. Statistical significance was determined using a paired t-test. Each dot represents a primary AML specimen. (D) Colony-forming potential of 2 CD34-enriched cord blood samples post scrambled or SIRT3 targeting siRNA transfection. CFU assay was prepared immediately after electroporation. Statistical significance was determined using a paired t-test. (E) Engraftment of AML24 post scrambled or SIRT3 targeting siRNA transfection. Each point represents a single mouse. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired t-test. (F) Engraftment of normal bone marrow post scrambled or SIRT3 targeting siRNA transfection. Each point represents a single mouse. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired t-test. All error bars represent standard deviation. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005, ****P<0.001; ns: not significant.