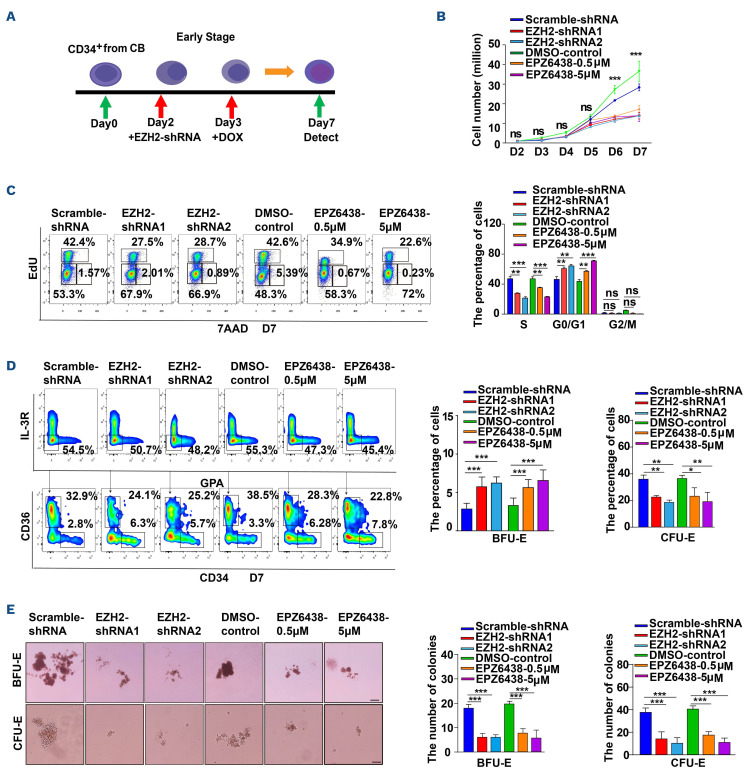
Figure 2.
Deficiency of EZH2 impaired cell growth and delayed differentiation during early stage of human erythropoiesis. (A) Schematic diagram of experiment method. The day of getting CD34+ cells was recorded as day 0. Lentivirus human CD34+ transduction at day 2. During the early stage erythroid development, small hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated knockdown was performed by using a tetracycline-inducible-GFP expression system, which can be induced by adding doxycycline (DOX) at day 3 or defunctionized EZH2 by treating cells with EPZ6438 at day 3. (B) Growth curves of cells, including scramble-shRNA, EZH2-shRNA, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) control, EPZ6438-0.5 mM, and EPZ6438-5 mM. (C) Representative flow cytometry profiles of the cell cycle as assessed by EdU and 7-AAD staining of day 7 erythroid cells. Quantitative analysis of the cell cycle from 3 independent experiments. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of erythroid progenitor cells at day 7. The fold change of absolute progenitor cells (burst-forming unit-erythroid [BFU-E] and colony-forming unit-erythroid [CFU-E]) number. (E) Colony-forming ability of erythroid cells derived from scramble-shRNA, EZH2-shRNA, DMSO control, EPZ6438 0.5 mM, and EPZ6438 5 mM in BFU-E colony medium or CFU-E colony medium on day 6; scale bar, 200 mm. Quantitative analysis the number of BFU-E and CFU-E colonies from 3 independent experiments. Statistical analysis is from 3 independent experiments, and the bar plot represents mean ± standard deviation of triplicate samples. ns: not significant; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.