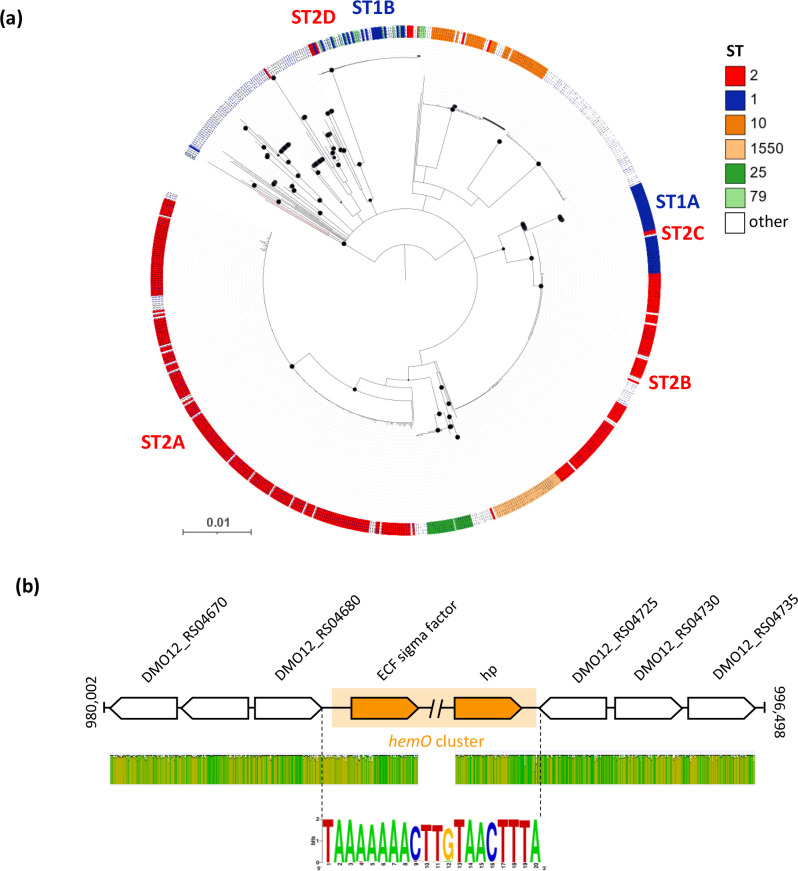
Fig. 6.
Evolution of the hemO clusters and genetic configuration of the hemO region in A. baumannii . (a) Neighbour-joining tree based on the alignment of concatenated sequences of the hemO gene cluster retrieved from 736 A . baumannii strains. STs are differentiated according to their colour code, as indicated in the key legend. Black-filled circles at the nodes denote bootstrap values ≥80 % (1000 replicates). The tree is midpoint rooted, and the scale bar represents the expected number of substitutions per site. The SDF branch is shown in red. (b) (top) The genomic context of the hemO gene cluster in A. baumannii ACICU. The orange-shaded region defines the boundaries of the hemO gene cluster, spanning from the ECF sigma to the hp gene (orange). The double slash denotes a region of hemO that is not shown. The gene map is not to scale. (b) (middle) Level of sequence identity of the hemO-flanking region among 732 and 729 hemO-posive genomes, including 3 upstream and 3 downstream genes, respectively. Green indicates 100 % identity, greeny-brown at least 30 % identity and red below 30 % identity. (b) (bottom) Consensus sequence of the 20 nt region between the hemO-flanking genes (DMO12_RS04680 and DMO12_RS04725, relative to the A. baumannii ACICU nomenclature) in 303 isolates lacking the hemO gene cluster, generated by the WebLogo representation (http://weblogo.threeplusone.com/ accessed January 2023). The first triplet (TTA) is the stop codon of the upstream gene (DMO12_RS04680), while the last triplet (TAA) is the stop codon of the convergent downstream gene (DMO12_RS04725). The height of the total stack indicates the degree of sequence conservation at a given position.