Fig. 4.
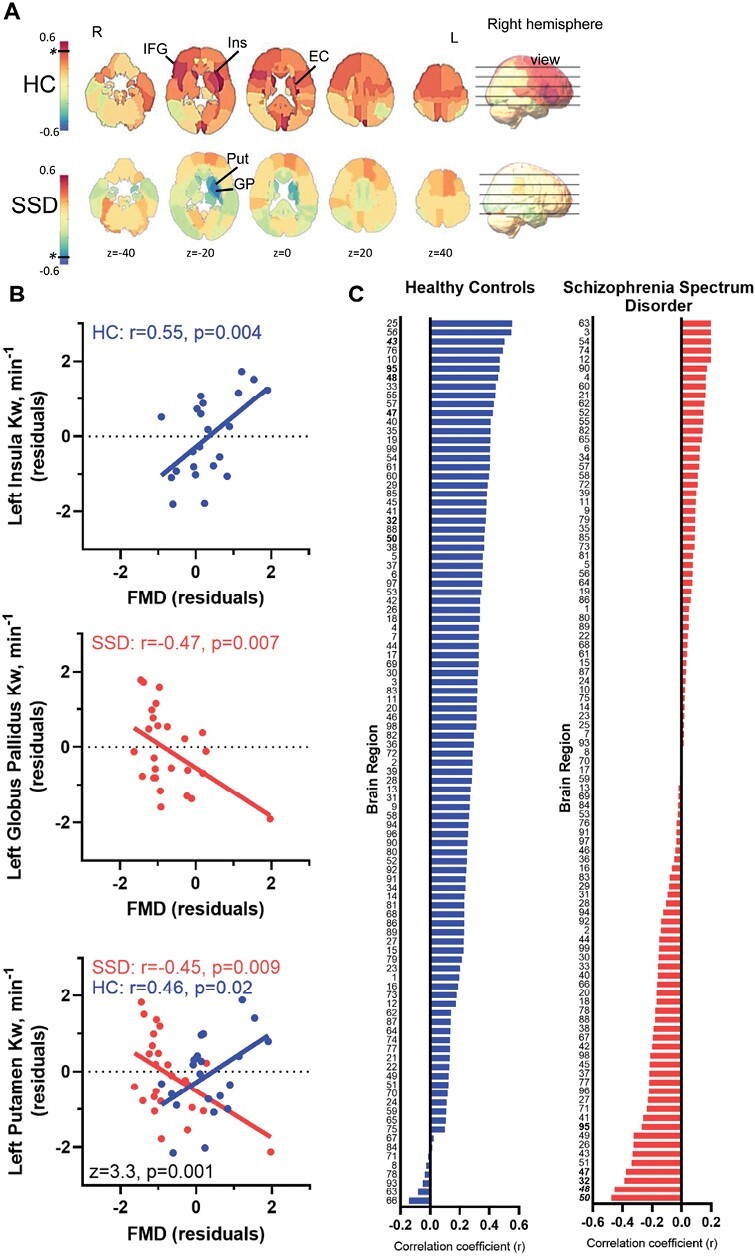
Relationship between peripheral vascular endothelial function and cerebral water exchange measurements. (A) Mapping the whole-brain distributions of the relationship between flow-mediated dilation and water exchange (Kw) examined by linear regressions based on partial Pearson correlation r-values (covaried for age and sex). Colder colors indicate negative r-values; warmer colors indicate positive r-values. The black horizontal line and * represents the color corresponding to the P < .01, in either positive or negative direction, if present. (B) The most significant association found in controls, left insula (top), and patients, left globus pallidus (middle), and the greatest group difference in the correlation coefficients between FMD and Kw, left putamen (bottom), were plotted. (C) 99 brain regions’ partial correlation coefficients (r), controlled for age and sex, arranged from greatest to least in HC (blue) and SSD (red) illustrating the overall pattern across brain regions. Names for each region are given in supplementary table 2. * significant r-value between FMD and Kw; # significant z-value for group differences in the correlation coefficients.
