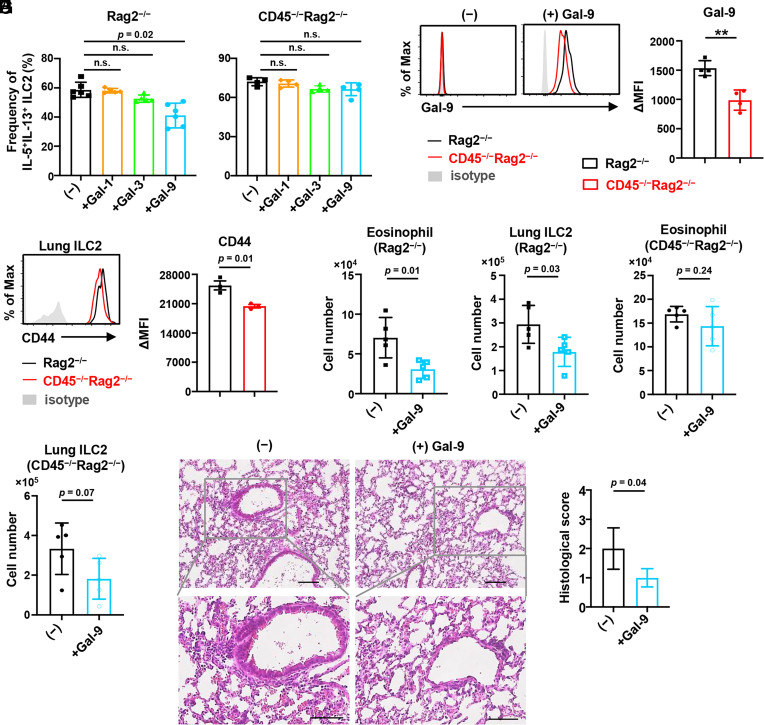
Fig. 6.
CD45-galectin-9 interaction influences the ILC2 suppression by CD45. (A) Frequency of IL-5+IL-13+ ILC2s from the lung of CD45−/−Rag2−/− and control Rag2−/− mice after ex vivo culture with IL-2, IL-7, IL-33, and with (+) or without (−) 5 µg/mL galectin (Gal)-1, Gal-3, or Gal-9 (n = 4 to 6). (B) Flow cytometric analysis of recombinant Gal-9 binding on the lung ILC2s and the mean fluorescence intensity difference (ΔMFI) between CD45−/−Rag2−/− and Rag2−/− mice after incubation with 1 µg/mL recombinant mouse Gal-9 for 30 min (n = 4). (C) Flow cytometric analysis for the expression of CD44 and ΔMFI between CD44 and isotype control in indicated lung ILC2s (n = 3). (D–G) Mice were administered 100 µg papain for 3 consecutive days to induce airway inflammation and with (+Gal-9) or without (−) 30 µg mouse recombinant Gal-9 on the second and third days. Numbers of eosinophils in BAL fluid (D) and ILC2s in the lung (E) of control Rag2−/− mice at day 4 (n = 5). Numbers of eosinophils in the BAL fluid (F) and ILC2s in the lung (G) of CD45−/−Rag2−/− mice at day 4. (n = 5). (H and I) H&E staining (H) and histological scores (I) of the lung from mice as shown in D and E (n = 4). (Scale bar, 100 µm.) Data represent at least two independent experiments with similar results (B, C, and H). Data are mean ± SD with one-way ANOVA (A) or Student’s t test (B–G and I) and pooled from two to three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; n.s., not significant.