Figure 1. CRISPR-Cas9 base editing screen targeting the spliceosome reveals several mutants sensitive or resistant to the small molecule spliceosome inhibitor pladienolide B.
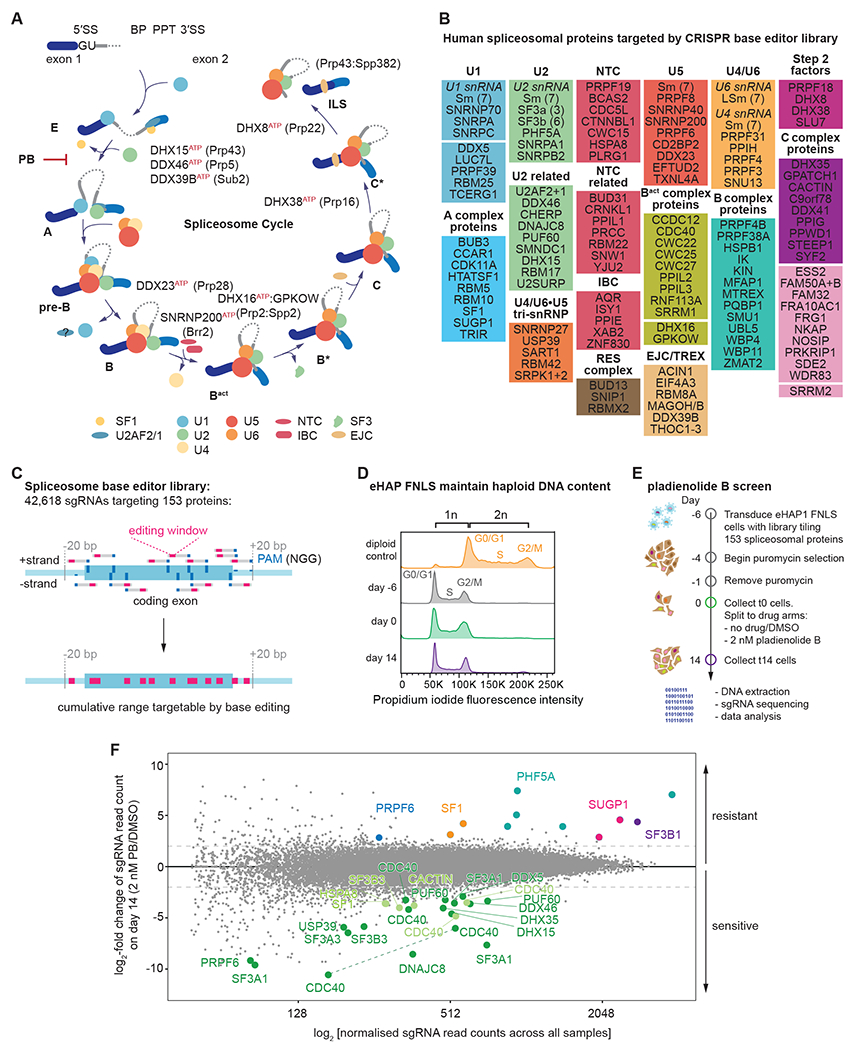
(A) Schematic of intron sequences required for splicing and the spliceosome cycle across the major assembly stages.
(B) List of spliceosomal genes targeted by the sgRNA library.
(C) Schematic of tiling sgRNA library. Every available PAM sequence (denoted in dark blue) on both strands of the genome is targeted across all coding exons.
(D) eHAP FNLS cell line can be maintained in a haploid state.
(E) Schematic of the pooled screen.
(F) Results of screen. MA-plot comparing day 14 of cells grown in presence or absence of 2 nM PB. For orientation lines indicate a log2-fold enrichment or depletion of two. sgRNA with strong sensitivity to PB are emphasized in green (dark green: p-adj < 0.05, light green: p-adj ≥ 0.05 but highly depleted). sgRNAs resulting in PB resistance are colored by protein target. For clarity, only data points for sgRNAs that passed the confirmation assay are shown. Dashed line: sgRNA targeting the same position and predicted to result in identical mutational outcome.
